FastTrack User Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction to FastTrack
- Why You Should Use FastTrack
- Purpose of this guide
- How to understand this guide
- Quick Start and Installation
- GUI Walkthrough
- Features
- Saving the data
- Editing the data file (For Advanced Users)
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction to FastTrack
FastTrack is an easy-to-use financial management desktop application designed for NUS SoC undergraduate students who are living on a tight budget.
With a combination of a Command Line Interface (CLI) and Graphical User Interface (GUI), our app provides a user-friendly and efficient way to track your expenses and manage your finances.
FastTrack prioritizes speed and efficiency to save your precious time and money, so you have more resources to spend on the important things in life.
Why you should use FastTrack
FastTrack is an expense tracking app that helps computing students keep track of their expenses by providing a simple and convenient command-line interface. Here are some reasons why you should consider using FastTrack:
-
Simplicity: FastTrack provides a simple and easy-to-use command-line interface that allows you to quickly add and track your expenses. This makes it ideal for computing students who prefer to use the command line to work with data.
-
Speed: FastTrack prioritizes speed and efficiency. With its command-line interface and all commands being a simple and one-line, it skips the hassle of clicking through screens like other expense tracking apps. The entire interface is shown in one screen.
-
Convenience: FastTrack can be used on any platform, including Windows, Mac, and Linux, making it convenient for computing students to track their expenses regardless of the platform they are using.
-
Customizable: FastTrack is highly customizable, allowing you to tailor it to your specific needs. You can add categories, set budgets, add recurring expenses, and even see statistics on your expenses.
-
Security: FastTrack is a locally hosted app that allows you to keep your expenses and financial information private. It does not require any personal information or financial details to use, ensuring that your information remains secure.
- Free and Open Source: FastTrack is a free and open-source app, meaning that it is available for download and use by anyone.
Purpose of this Guide
This User Guide provides information on how to use FastTrack. It includes:
- Installation and setup of app
- Detailing features of the app
- Usage of app and its commands
- Tips, tricks and warnings on usage of commands
- Troubleshooting tips
- Answering Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding this guide
Icons
Throughout FastTrack’s user guide, you may encounter unfamiliar symbols. This is a quick overview of what these symbols mean and what to look out for.
| Icon | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Warning | |
| Information | |
| Tip |
Warning Box
![]() Warning:
Danger zone! Do pay attention to the information here carefully. Careless usage of this function may cause certain
things to not work as expected.
Warning:
Danger zone! Do pay attention to the information here carefully. Careless usage of this function may cause certain
things to not work as expected.
Information Box
Tip Box
![]() Tip:
This provides some quick and convenient hacks that you can use to optimize your experience with FastTrack.
Tip:
This provides some quick and convenient hacks that you can use to optimize your experience with FastTrack.
Quick start and Installation
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
fastTrack.jarhere. -
Drag the file into a folder you want to use as the home folder for FastTrack.
-
Double-click the FastTrack JAR file to run the application.
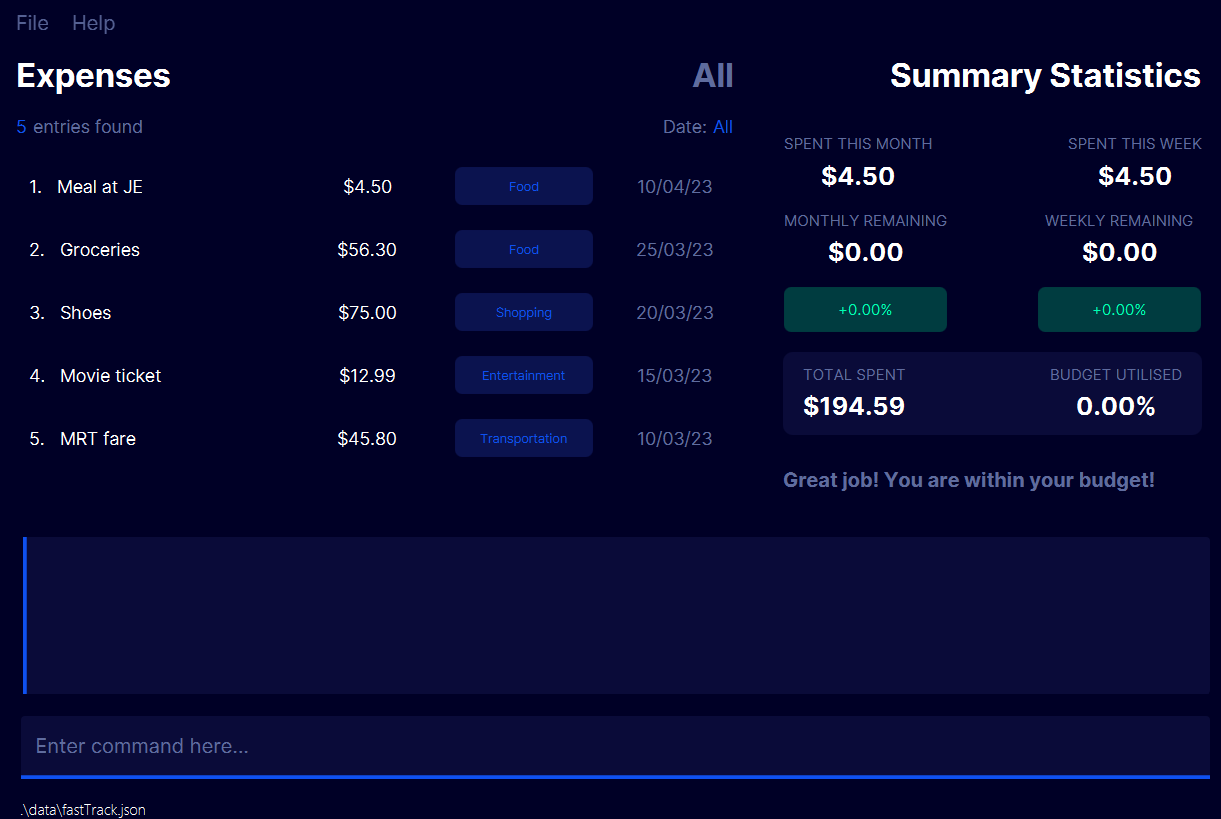
A Graphical User Interface (pictured below) will appear. Note how the app contains some sample data.
-
Type a command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try:-
list: Lists all expenses -
clear: Clears the sample data -
add c/groceries n/milk p/4.50 d/14/2/23: Adds an expense namedmilkto the expenses list with a price of $4.50 and a date of 14/02/2023 -
delete 3: Deletes the 3rd expense shown in the current list -
exit: Exits the app
-
-
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Walkthrough
The following diagrams highlight the different sections of the Graphical User Interface (GUI) of FastTrack.
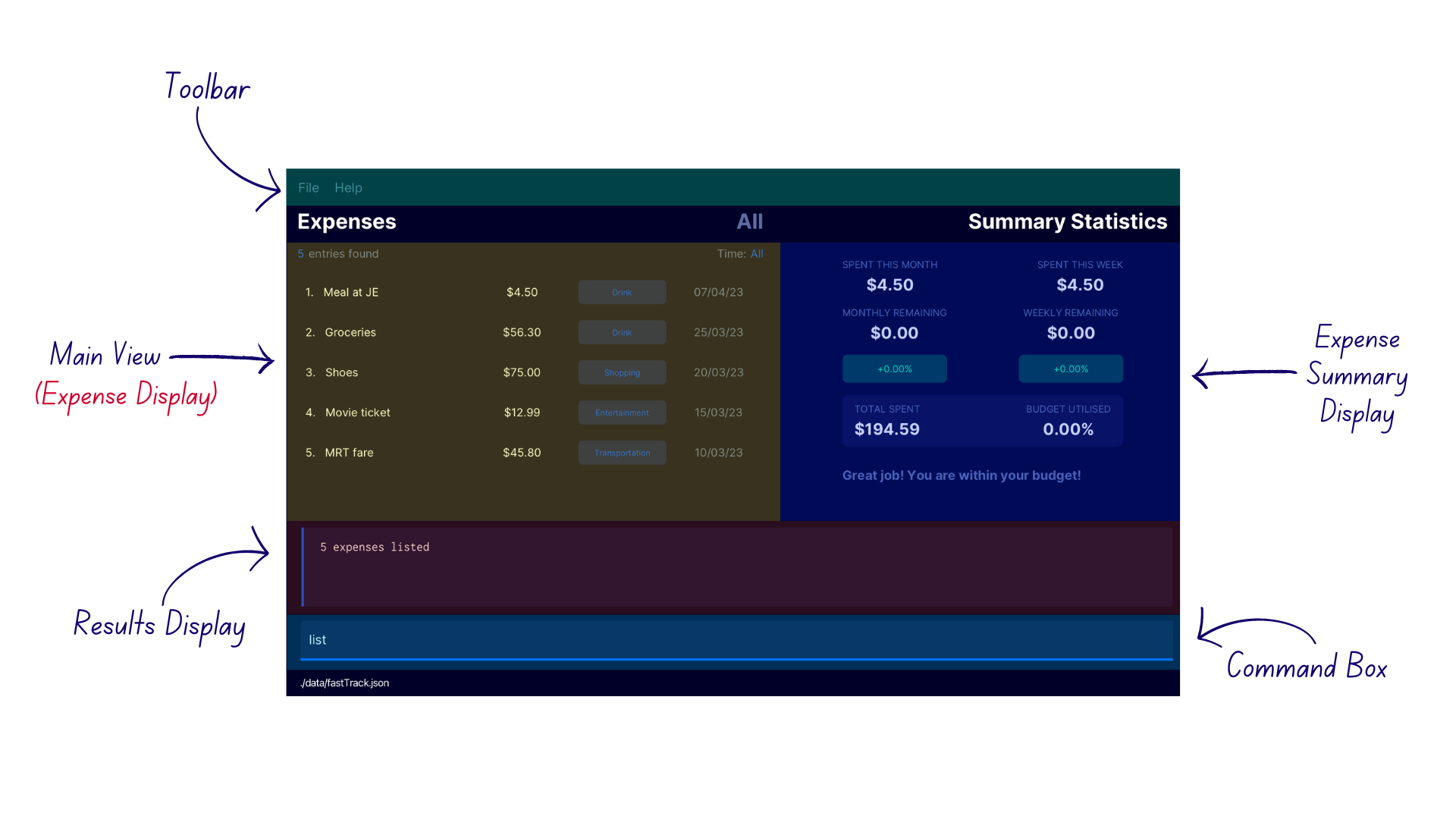 The main display. It displays all added expenses on the left, showing each expense’s price, category and date added.
The main display. It displays all added expenses on the left, showing each expense’s price, category and date added.
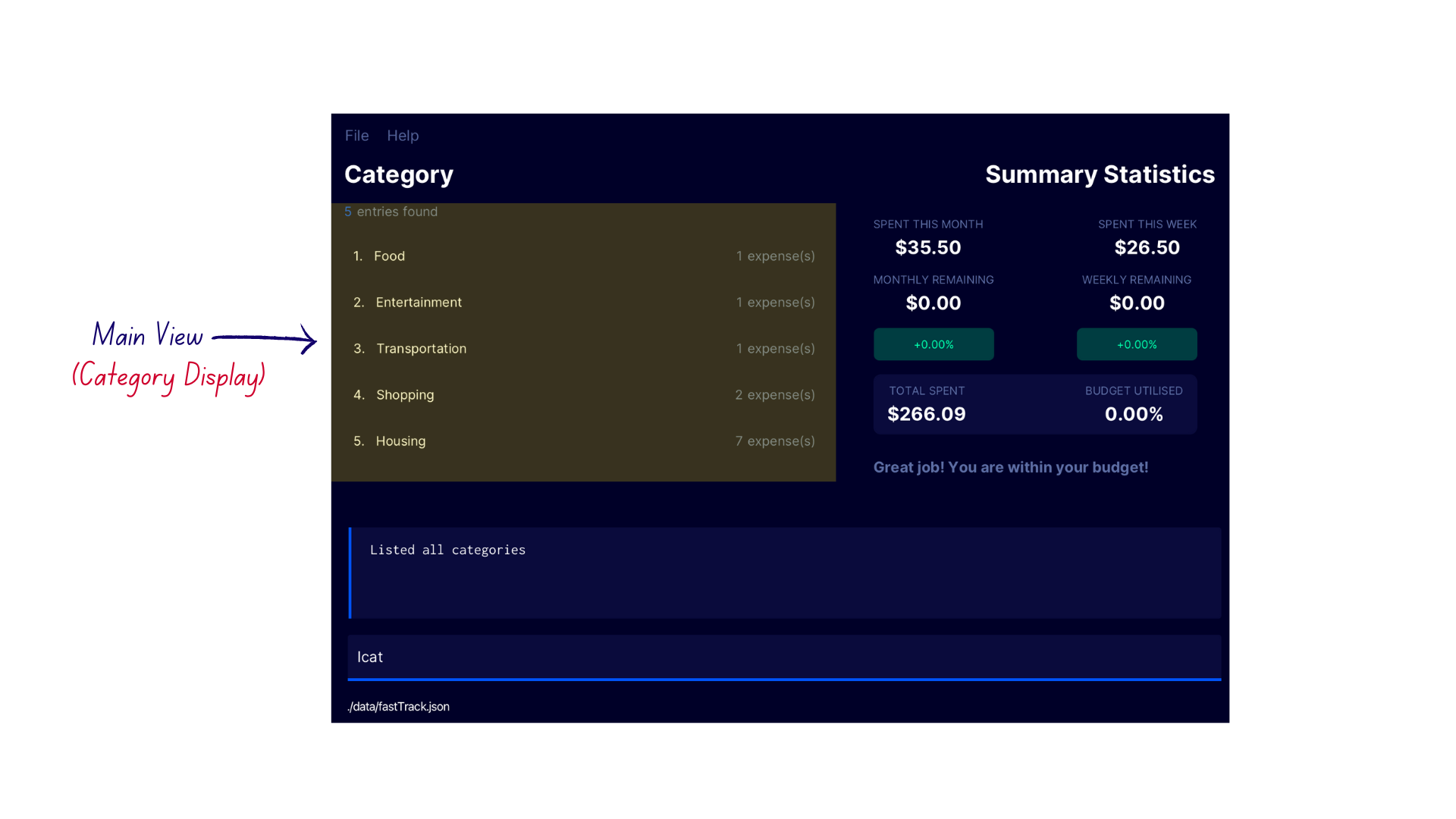 The Category display. It shows all currently added Categories for expenses. This display is shown only after using the
command to list categories.
The Category display. It shows all currently added Categories for expenses. This display is shown only after using the
command to list categories.
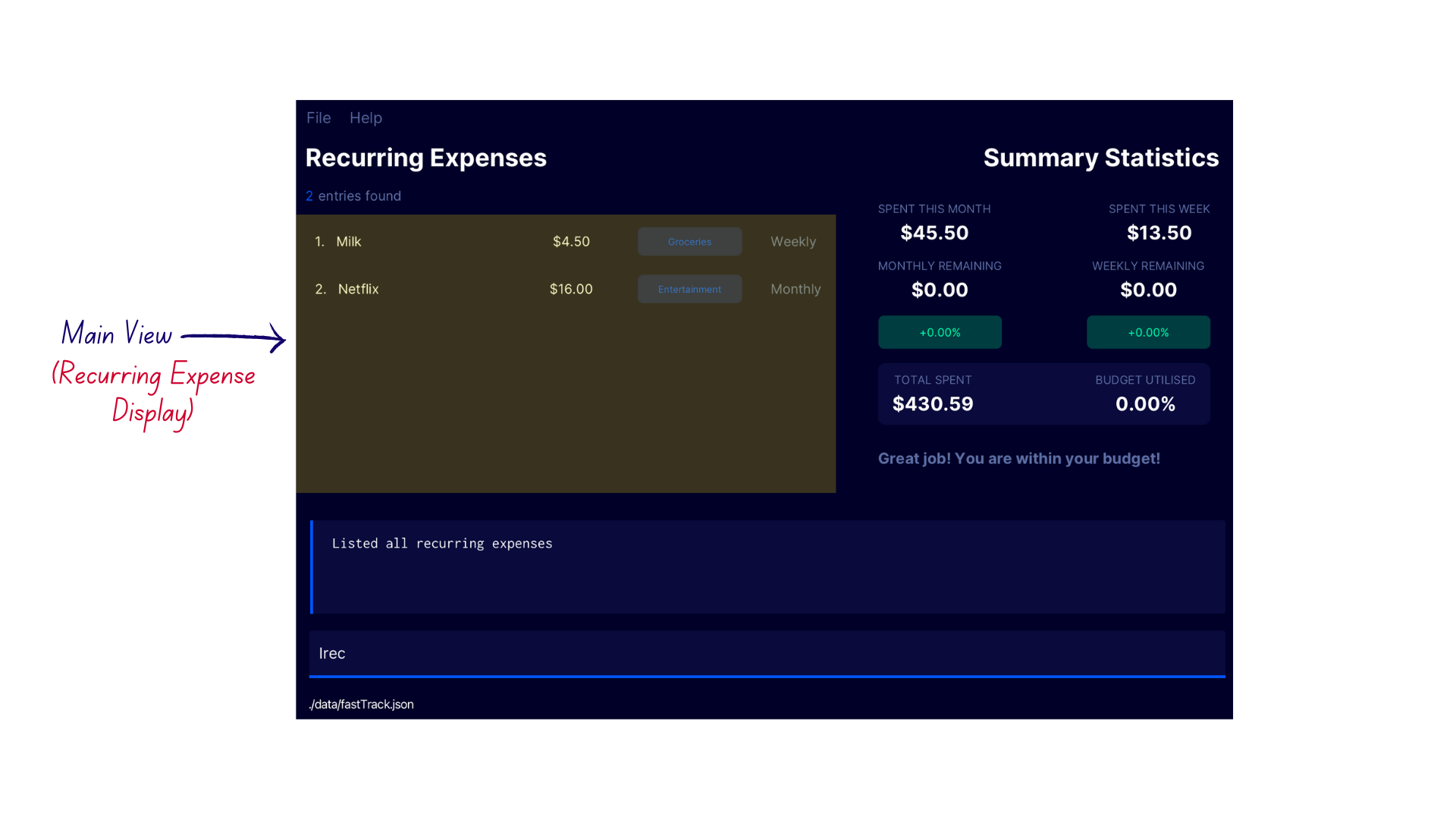 The Recurring Expense display. It shows all currently added Recurring Expenses. This display is shown only after using the
command to list recurring expenses.
The Recurring Expense display. It shows all currently added Recurring Expenses. This display is shown only after using the
command to list recurring expenses.
| FastTrack UI Part | Description |
|---|---|
| One-time Expense Display | Displays the list of saved one-time expenses with filters applied (if any). This display occupies the Main View section. |
| Category Display | Displays the list of saved categories, including the number of expenses associated with each category. This display occupies the Main View section. |
| Recurring Expense Display | Displays the list of saved recurring expenses. This display occupies the Main View section. |
| Results Display | Displays feedback from the application after entering a command, which can be used to indicate the outcome of the command. It provides guidance for the user, especially if a command has failed. |
| Command Box | A text input field where you can type in a command for FastTrack to execute. |
| Expense Summary Display | A visual display containing expense statistics (Refer to the feature Expense Statistics below for details. |
| Toolbar | Contains buttons which allow you to access the user guide and exit from the application. |
Features
The features of FastTrack can be divided into 4 groups, Category Features, Expense Features, General Features and Expense Statistics Feature. With these 4 groups in mind, remembering the different commands becomes extremely convenient, as each group contains mainly 4 types of operations - add, delete, edit and list!
Commands
Other Notable Features
Command Syntax
First-time users may have difficulty understanding the syntax described in the command instructions.
If you are new to using a Command Line Interface (CLI), we recommend reading this brief section before using FastTrack. Understanding the CLI will help you enter commands more efficiently, which can save you time in the long run.
In simple terms, the Command Line Interface (CLI) is a way to interact with FastTrack by typing in commands using just one line of text. This means you can add expenses quickly and easily.
Here is a quick guide on how to read the syntax mentioned in the User Guide for using FastTrack’s commands.
command tag1/ PARAMETER_1 tag2/ PARAMETER_2 [tag3/ PARAMETER_3]
| Element | Format | Usage |
|---|---|---|
command |
Name of command eg. add, find
|
Specifies the command to be executed. |
tag/ |
Prefix for a field, followed by /
|
Specifies which field given input argument is for |
PARAMETER |
Words that are in UPPERCASE | Specifies user input for field specified by tag/ e.g. In add c/CATEGORY_NAME, CATEGORY_NAME is a parameter, which the user decides is “groceries”. The final command will be entered as add c/groceries. |
[] |
Square brackets around tag/ and PARAMETER
|
Indicates that field specified by tag/ is optional and may be omitted. If left unspecified, it will be set to a default value. |
For example, the command format for add:
add c/CATEGORY_NAME n/ITEM_NAME p/PRICE [d/DATE]
-
addis thecommandname. -
c/,n/,p/,d/aretag/s to denote fields of category, name, price and date respectively. -
CATEGORY_NAME,ITEM_NAME,PRICE,DATEarePARAMETERSto be supplied to the aforementionedtag/s. -
[d/DATE]indicates that the field for the date is optional.
Don’t worry if it takes a bit of time to get used to the commands. Once you’re familiar with the commands, you’ll be able to add expenses quickly and easily.
![]() Information about the command format
Information about the command format
Before diving further into the guide, here are some things to take note about the way we formatted commands for FastTrack in this user guide.
-
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesc/CATEGORY_NAME p/PRICE,p/PRICE c/CATEGORY_NAMEis also acceptable. -
If a parameter is expected only once in the command, but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be taken.
e.g. if you specifyp/4.50 p/5.80, onlyp/5.80will be taken. -
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,exit) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123, it will be interpreted ashelp.
![]() Warning about Date Formatting:
Warning about Date Formatting:
Some commands may include the entry of a DATE, like the add command or the addrec command. A specific date format, Day/Month/Year should be used to format the date provided.
However, if the day is within 1-31 but not a valid date, e.g. 30th February, FastTrack will smartly correct your date provided to the last date of the month.
i.e, 30/2/2023 will be corrected to 28/2/2023.
Category Features
FastTrack makes it easy for you to keep track of your spending by organizing expenses into categories. A category is like a folder that holds all your expenses that fall under a specific theme. For example, you might have a category called Groceries where you record all purchases from Fairprice or NTUC.
To create a category in FastTrack, simply give it a name, such as Entertainment or Transportation. You can also add a short text summary to give yourself more context about the category.
FastTrack even has a default Misc category for any expenses that you haven’t categorized yet, however, this category is not modifiable or accessible.
![]() Info
Info
Note that category names in FastTrack are case-insensitive. For example, a category named Groceries will be treated as the exact same category as groceries.
Command Summary
| Feature | Command Format | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| List Categories | lcat |
lcat |
| Add Category | addcat c/CATEGORY_NAME s/SUMMARY |
addcat c/Groceries s/for living |
| Delete Category | delcat INDEX |
delcat 1 |
| Edit Category | edcat INDEX [c/CATEGORY_NAME] [s/SUMMARY] |
edcat 1 c/New Name s/New Summary |
| Category Summary | sumcat INDEX |
sumcat 2 |
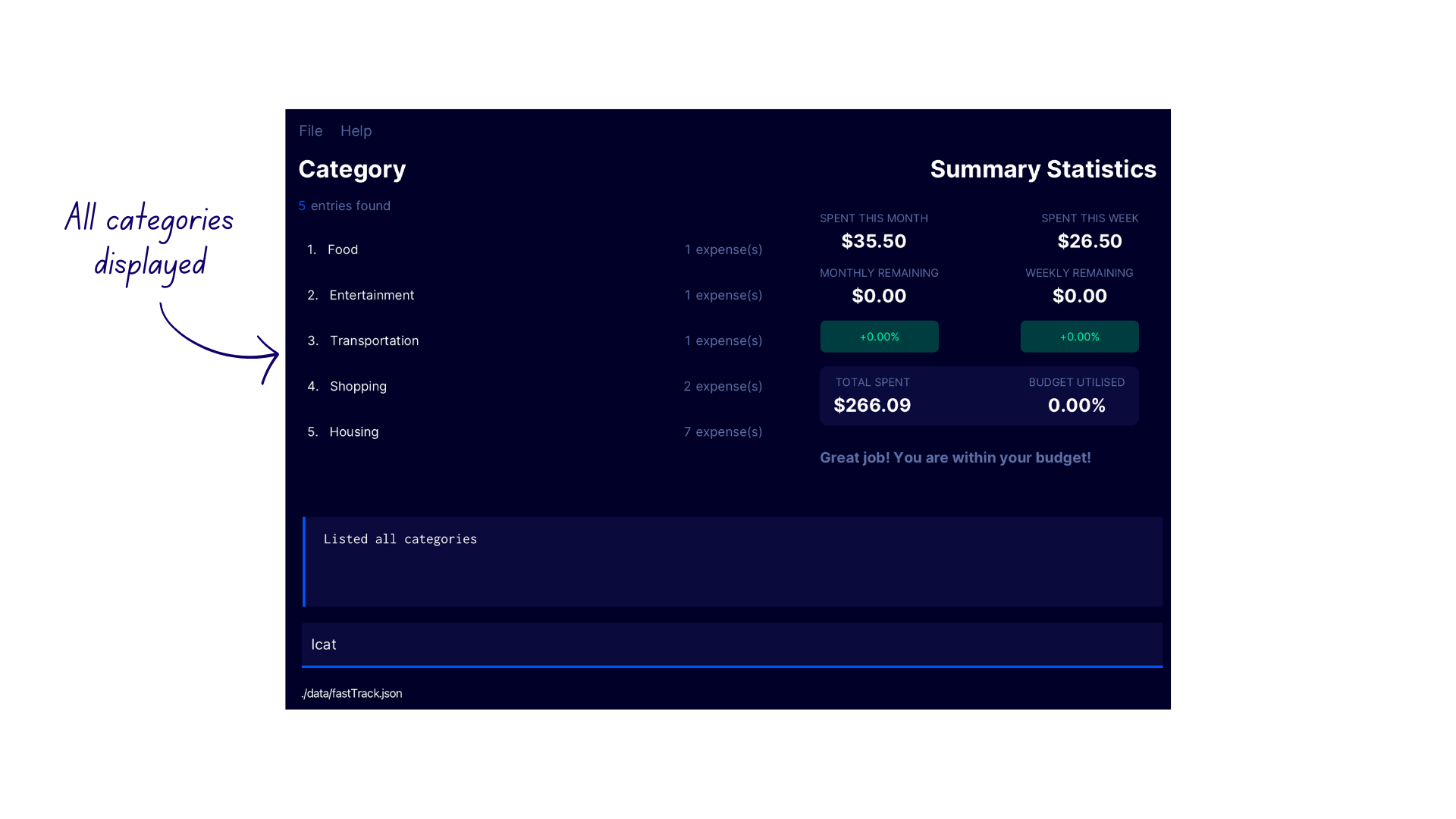
Listing Categories lcat
Displays the list of categories in FastTrack.
Format: lcat
Demonstration
- Type
lcatinto the command box - FastTrack displays the list of categories with the confirmation message
Listed all categories
Adding a category addcat
Adds a new category to FastTrack. If a category with the same name already exists, this command will not execute.
Format: addcat c/CATEGORY_NAME s/SUMMARY
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
CATEGORY_NAME |
Title of the category to be added. |
SUMMARY |
Short summary of what this category keeps track of. |
Examples
-
addcat c/Groceries s/for livingcreates a newGroceriescategory with the summary offor living. -
addcat c/Entertainment s/for fun!creates a newEntertainmentcategory with the summary offor fun!.
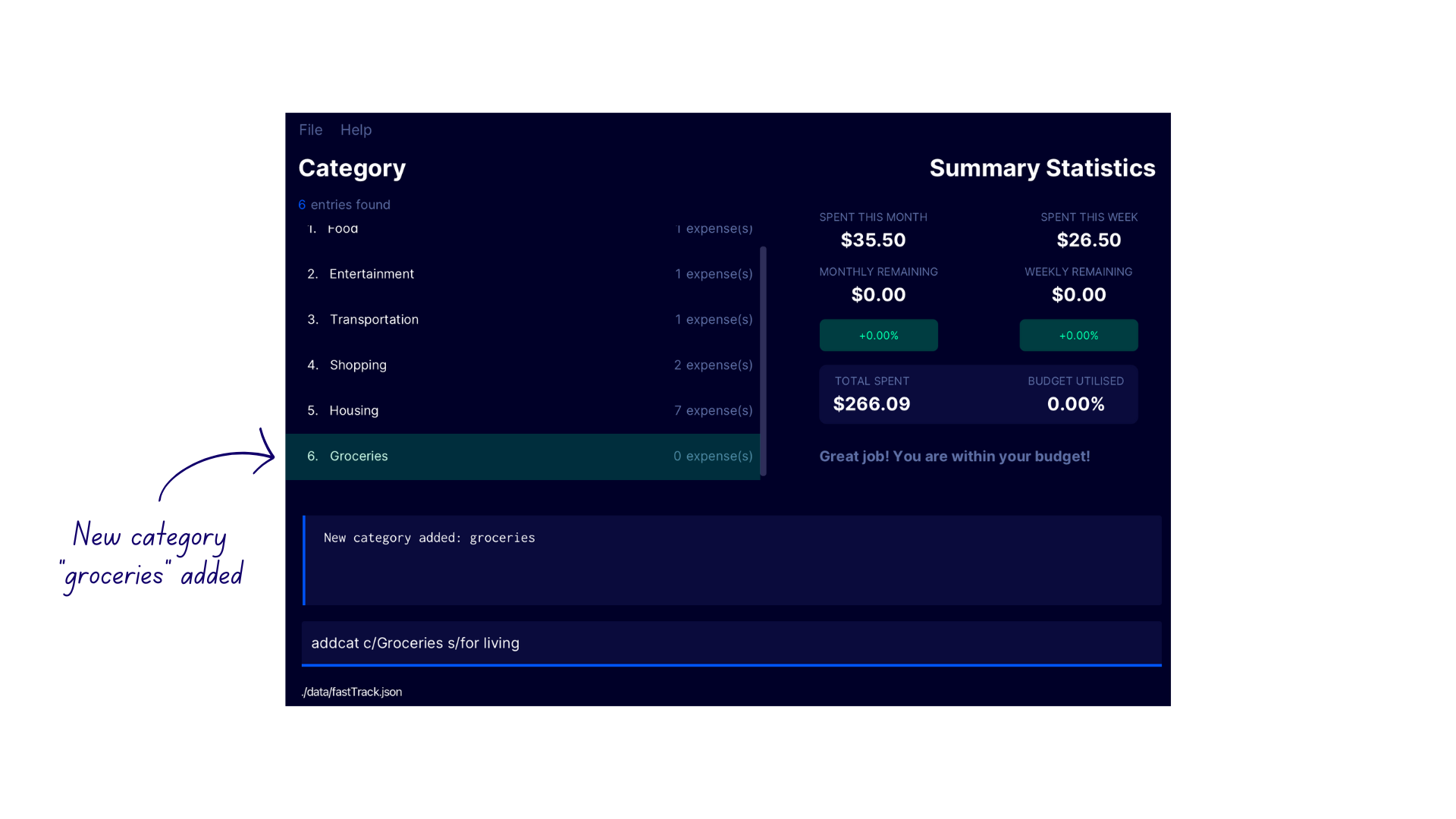
Demonstration
- Enter the command
lcatto switch to the Category Display - Enter the command
addcat c/Groceries s/for livinginto the command box - FastTrack adds the new category to the category list with the confirmation message
New category added: groceries
Deleting a category delcat
Deletes the category at the specified INDEX in the category list.
Format: delcat INDEX
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
INDEX |
The index number shown in the displayed category list. It must be a positive integer i.e. 1, 2, 3, … Expenses previously categorised under the specified category will be automatically re-categorized under the Misc category. |
![]() Info:
Info:
If you delete a category that has existing expenses associated with it, those expenses will be automatically reassigned to the default internal Misc category. But don’t worry! You can still re-assign them later with the edit expense command. To avoid losing track of expenses, we recommend that you review and update your categories periodically, rather than deleting them altogether.
Examples
-
lcatfollowed bydelcat 2deletes the second category in the category list -
lcatfollowed bydelcat 1deletes the first category in the category list
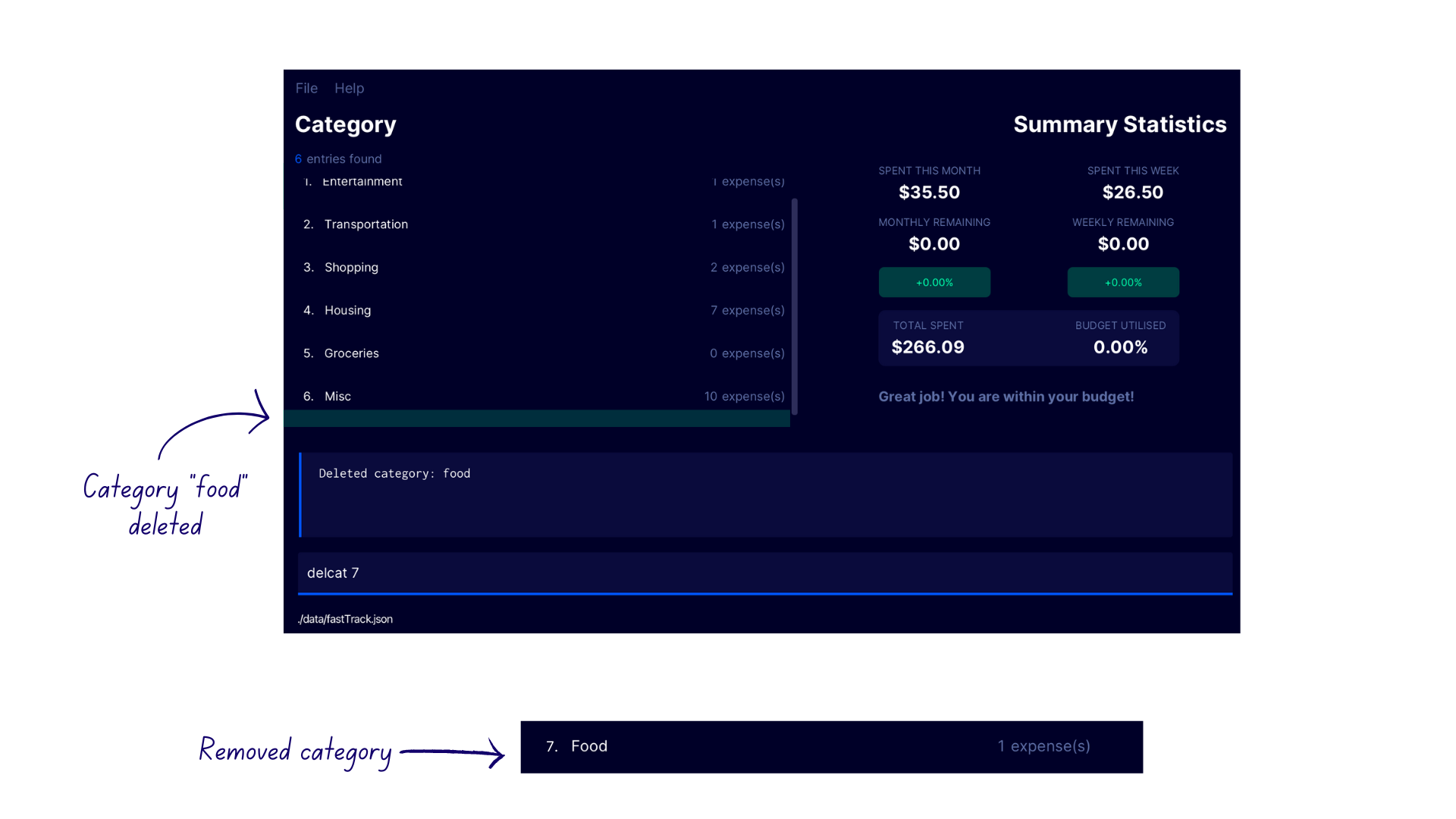
Demonstration
- Enter the command
lcatto switch to the Category Display - Enter the command
delcat 7into the command box - FastTrack deletes the seventh category
Foodfrom the category list with the confirmation messageDeleted category: food
Editing a category edcat
Edits the category at the specified INDEX in the category list.
Format: edcat INDEX [c/CATEGORY_NAME] [s/SUMMARY]
Both CATEGORY_NAME and SUMMARY are optional by themselves, but at least one of them must be specified in addition
to INDEX, otherwise the command will not be executed.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
INDEX |
The index of the category to be edited. It must be a positive integer i.e. 1, 2, 3, … |
CATEGORY_NAME |
The new name of the category being edited at the specified index. This parameter is optional. |
SUMMARY |
The new summary of the category being edited at the specified index. This parameter is optional. |
Examples
-
edcat 1 c/Drinkchanges the name of the first category in the category list toDrink -
edcat 2 c/Food s/Eating outchanges the name and summary of the second category in the category list toFoodandEating outrespectively.
Demonstration
- Enter the command
lcatto switch to the Category Display - Enter the command
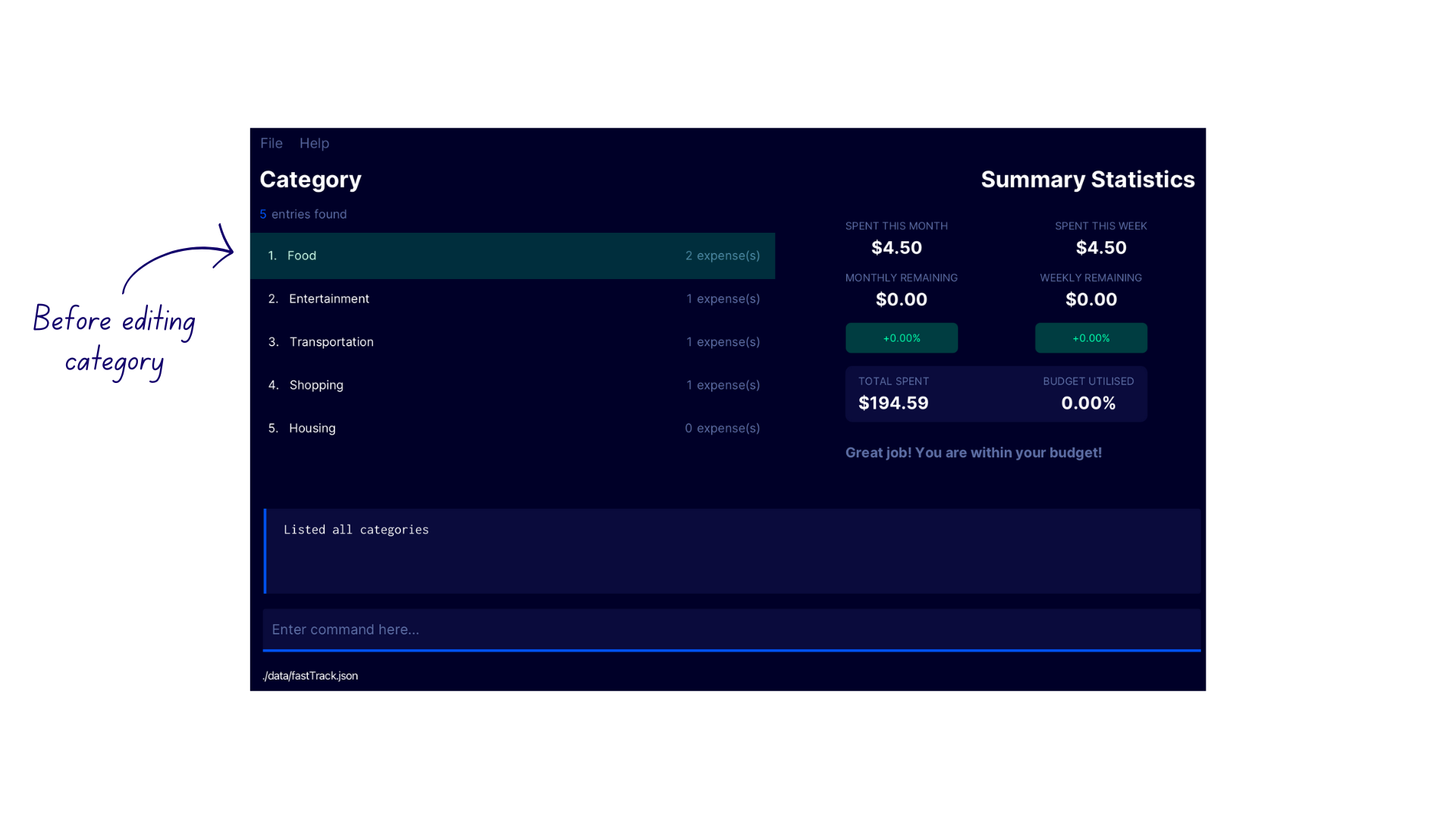
edcat 1 c/Drinkinto the command box - FastTrack edits the name of the first category
Foodfrom the category list toDrinkwith the confirmation messageEdited category: Drink
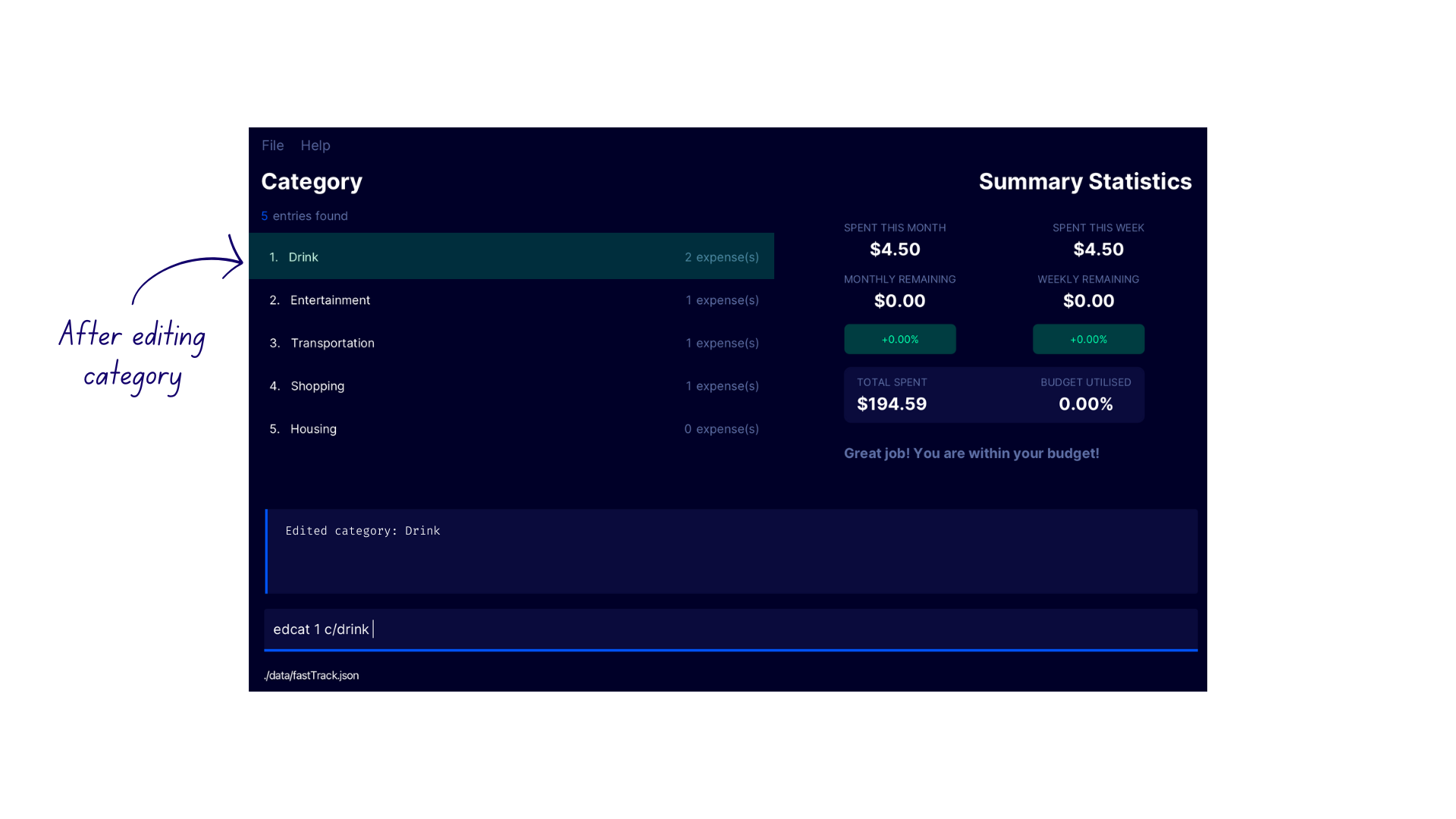
Viewing Category Summary sumcat
Displays the category summary for a category.
Format: sumcat INDEX
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
INDEX |
The index of the category to be edited. It must be a positive integer i.e. 1, 2, 3, … |
Demonstration
- Enter the command
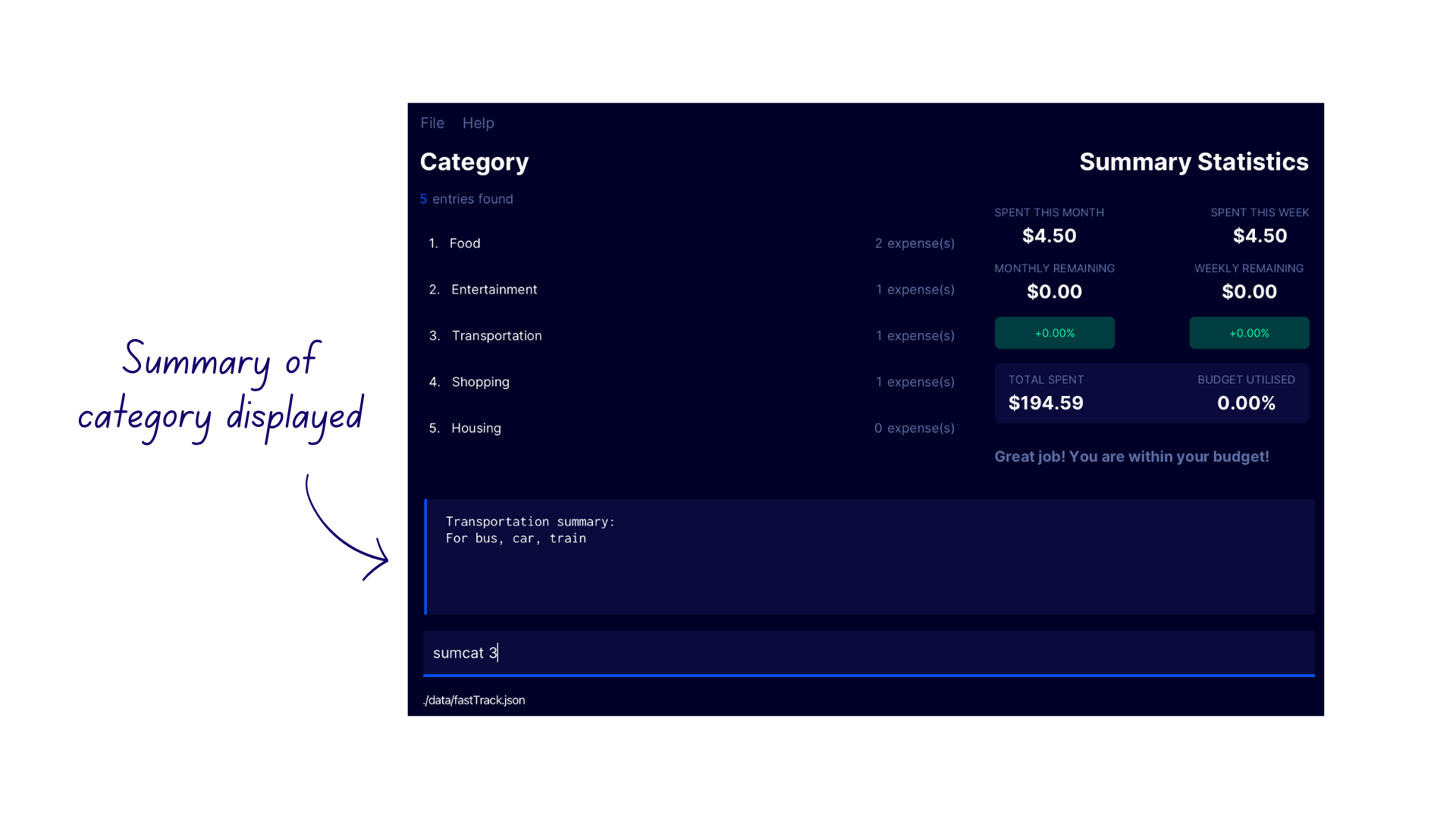
lcatto switch to the Category Display - Enter the command
sumcat 2into the command box. - FastTrack displays the summary of the Entertainment category in the Results Display.
Expense Features
An expense is a single purchase that you want to track. Each expense has a name, price, category, and date. With FastTrack, you can easily duplicate an expense if you happen to make the same purchase multiple times, such as buying a coffee from CoolSpot every morning on your way to NUS.
Finally, there are recurring expenses. These are expenses that are charged on a regular basis, such as a monthly subscription to Netflix or an annual Heroku subscription. Instead of manually creating an expense every time the payment is due, you can set up a recurring expense in FastTrack. Simply specify the start date, interval (daily, weekly, monthly, yearly), and end date (if applicable), and FastTrack will automatically generate the expenses for you.
Command Summary
One-time Expenses
| Feature | Command Format | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| List Expenses | list [c/CATEGORY_NAME] [t/TIMEFRAME] |
list c/Food t/month |
| Add Expense | add c/CATEGORY_NAME n/ITEM_NAME p/PRICE [d/DATE] |
add c/Food p/20 n/Mac d/14/2/23 |
| Delete Expense | delete INDEX |
delete 1 |
| Edit Expense | edexp INDEX [c/CATEGORY_NAME] [n/EXPENSE_NAME] [d/DATE] [p/PRICE] |
edexp 1 c/Food n/Mac d/20/4/23 p/10 |
| Find Expense | find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] |
find KFC chicken |
Recurring Expenses
| Feature | Command Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| List Recurring Expense | lrec |
lrec |
| Add Recurring Expense | addrec c/CATEGORY_NAME n/ITEM_NAME p/PRICE t/INTERVAL sd/START_DATE [ed/END_DATE] |
addrec c/Shows n/Netflix p/10 t/month sd/10/3/23 ed/10/03/24 |
| Delete Recurring Expense | delrec INDEX |
delrec 1 |
| Edit Recurring Expense | edrec INDEX [c/CATEGORY_NAME] [n/EXPENSE_NAME] [p/PRICE] [t/INTERVAL] [ed/END_DATE] |
edrec 1 c/Show n/Disney Plus p/2 t/week ed/10/5/24 |
One-Time Expenses
Listing expenses list
The list feature in FastTrack allows you to view all your expenses. You can filter the list based on specific categories and timeframes to get a more customized view of your spending.
If you apply the CATEGORY_NAME filter, only expenses associated with that particular category will be displayed. For instance, if you filter by groceries, you’ll only see the expenses you’ve categorized as groceries.
If you apply the TIMEFRAME filter, you can see expenses that fall within a particular time period. For example, you could filter by month to see only the expenses you incurred in the current month.
If you don’t specify any filters, the expense list will show all your expenses by default.
Format: list [c/CATEGORY_NAME] [t/TIMEFRAME] [r/RECUR_PERIOD]
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
CATEGORY_NAME |
The name of the category of which expenses are classed under. This parameter is optional. |
TIMEFRAME |
The timeframe of which expenses were added. The timeframes available are: 1. week (alias: w) 2. month (alias: m)3. year (alias: y)This parameter is optional. |
![]() What is a timeframe?
What is a timeframe?
A TIMEFRAME allows you to set a specific interval to filter your expenses. t/w or t/week is a timeframe representing the current week, while t/m or t/month is a timeframe representing the current month, and t/y or t/year is a timeframe representing the current year.
Examples
listlist c/Groceries t/weeklist c/Entertainment t/monthlist c/Foodlist t/wlist c/Entertainment t/year
Demonstration
List Expenses by Category
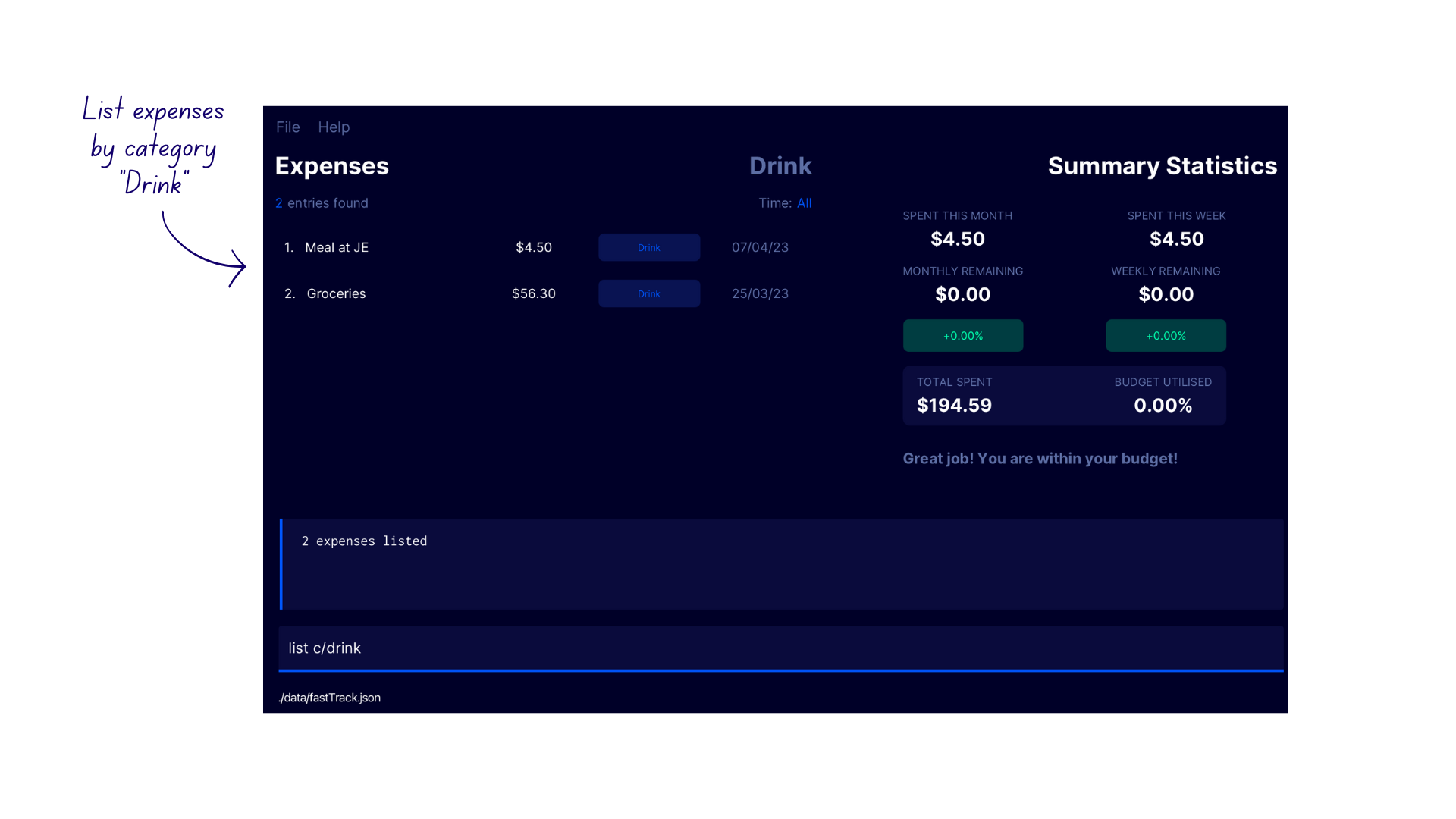
- Enter the command
list c/drinkinto the command box - FastTrack displays the expenses under the category
Drinkwith the confirmation message2 expenses listed. The number of expenses may differ for every user.
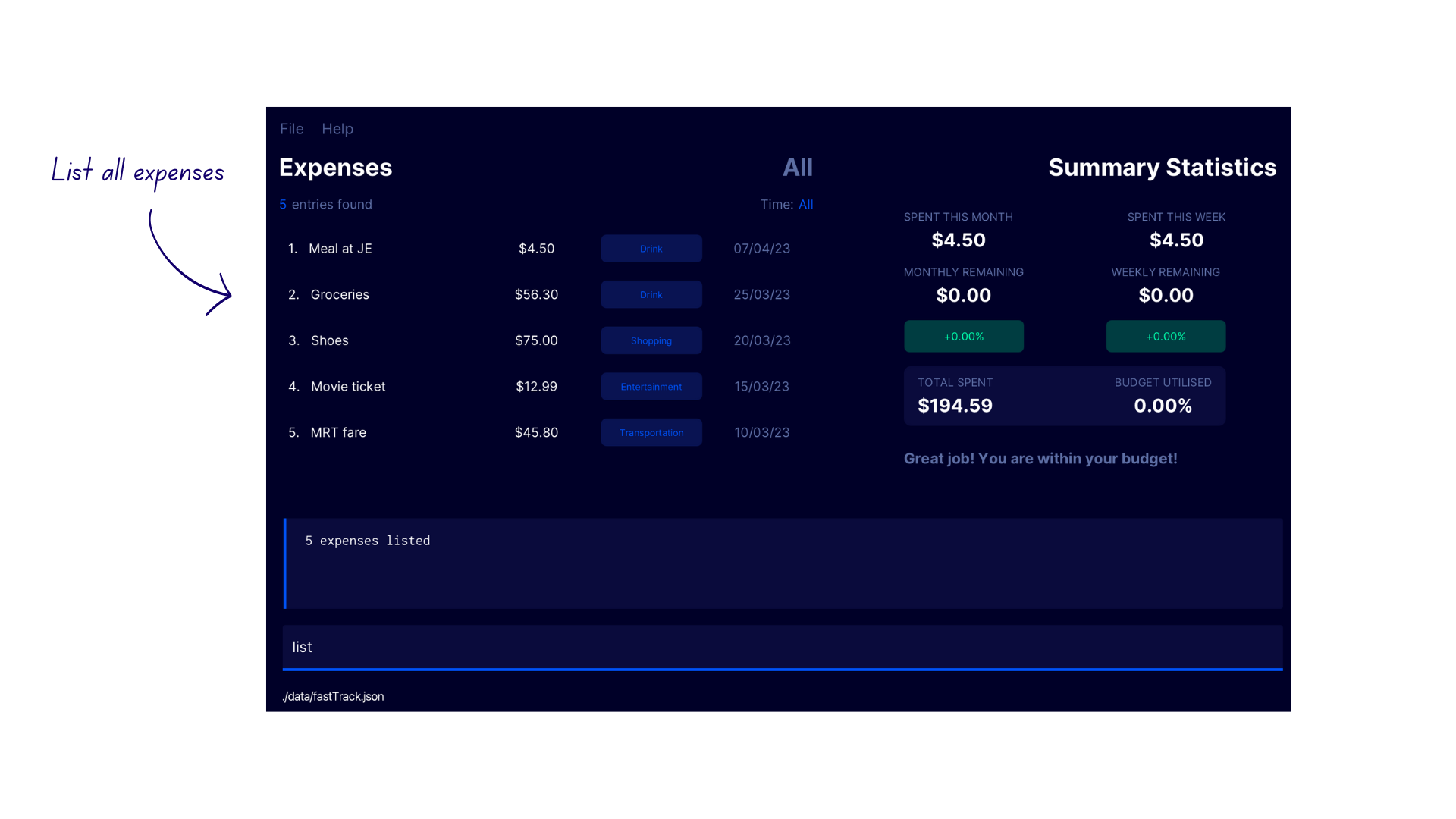
List All Expenses
- Enter the command
listinto the command box - FastTrack displays all expenses with the confirmation message
5 expenses listed. The number of expenses may differ for every user.
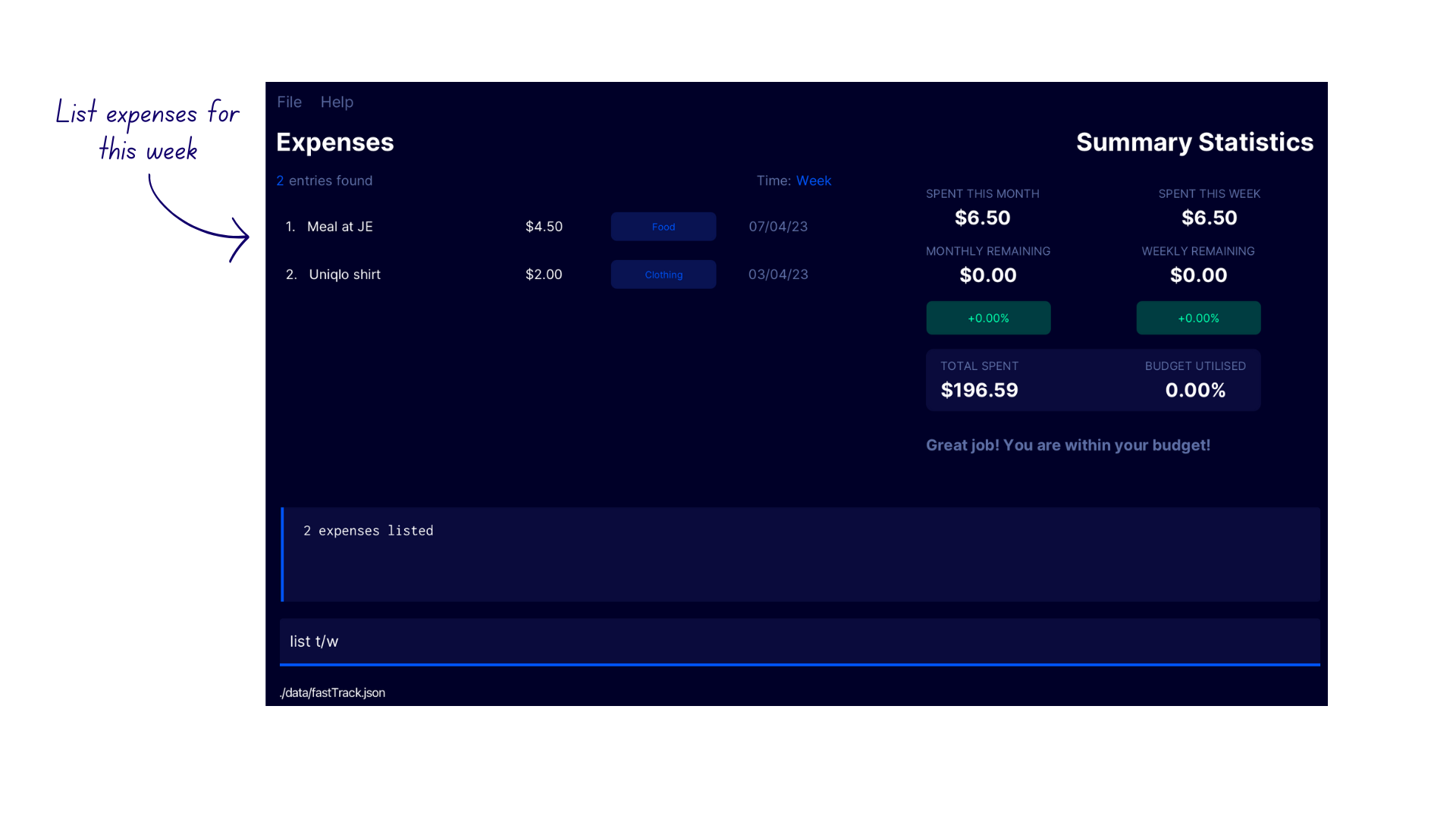
List Expenses by Timeframe
- Enter the command
list t/winto the command box - FastTrack displays all expenses within the current week with the confirmation message
2 expenses listed. The number of expenses may differ for every user.
![]() Using both
Using both CATEGORY_NAME and TIMEFRAME filters:
- Using both the category and timeframe filters will only display expenses that satisfy both the filter conditions.
e.g. inlist c/food t/week, only expenses with both the category name “Food” and date falling within the current week will be displayed.
Adding an expense add
Adds a new one-time expense to FastTrack.
Format: add c/CATEGORY_NAME n/ITEM_NAME p/PRICE [d/DATE]
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
CATEGORY_NAME |
The category which the expense should be classified under. If there is no such category in FastTrack, a new category will be created with the specified category name. |
ITEM_NAME |
Name of the expense being added. |
PRICE |
The price of the expense being added. The specified price should be a number, e.g. 4, 4.50. |
DATE |
The date of the expense being added. The date format should be d/m/yyyy. This is an optional input, and if left unspecified, the date of the expense will be set to the current date by default. |
Examples
add c/groceries n/milk p/4.50add c/entertainment p/20 n/movie night d/14/2/23
Demonstration
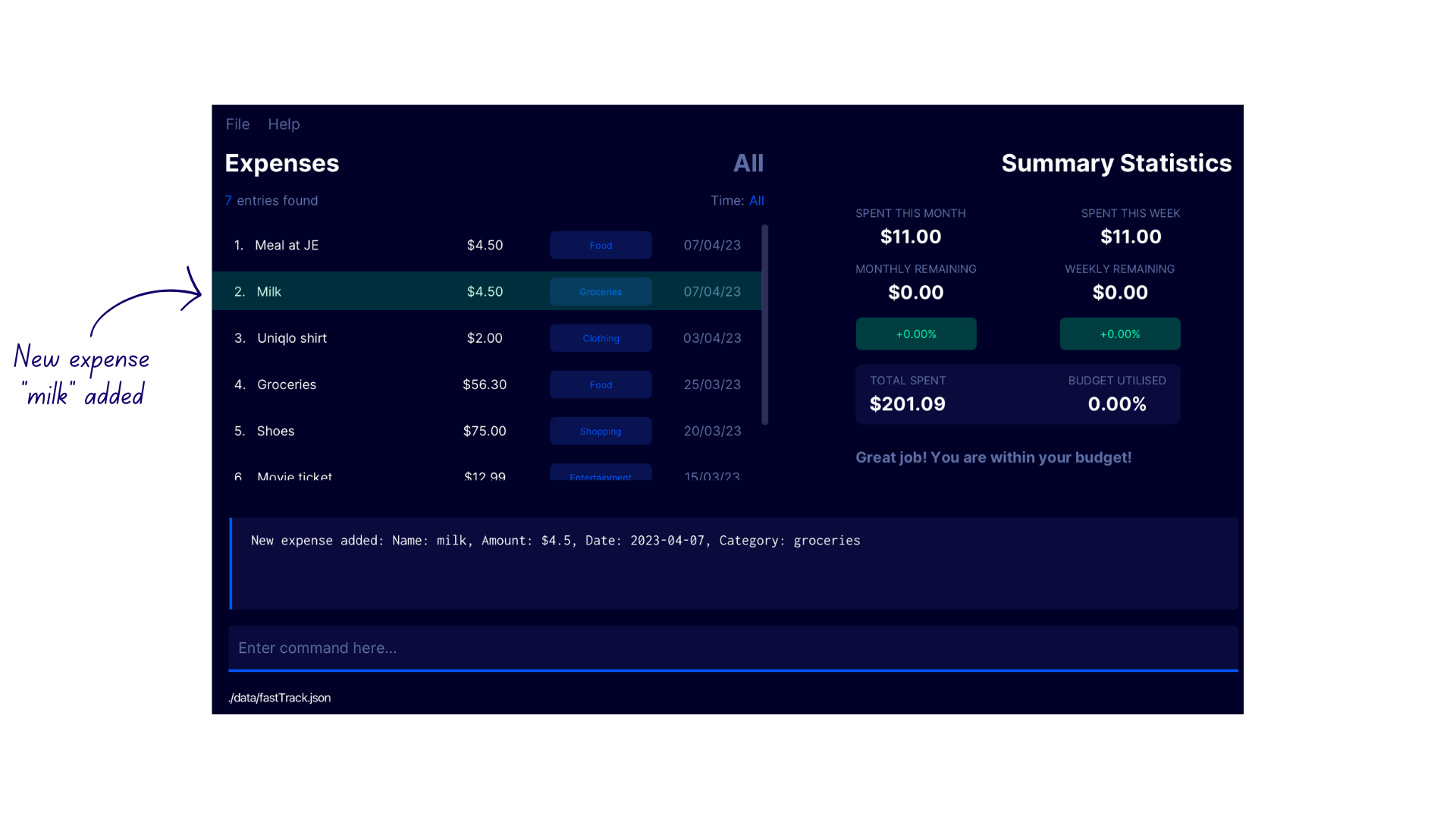
- Enter the command
add c/groceries n/milk p/4.50into the command box - FastTrack adds the new expense under the new category
Grocerieswith the confirmation messageNew expense added: Name: milk, Amount: $4.5, Date: 2023-04-07, Category: groceries.
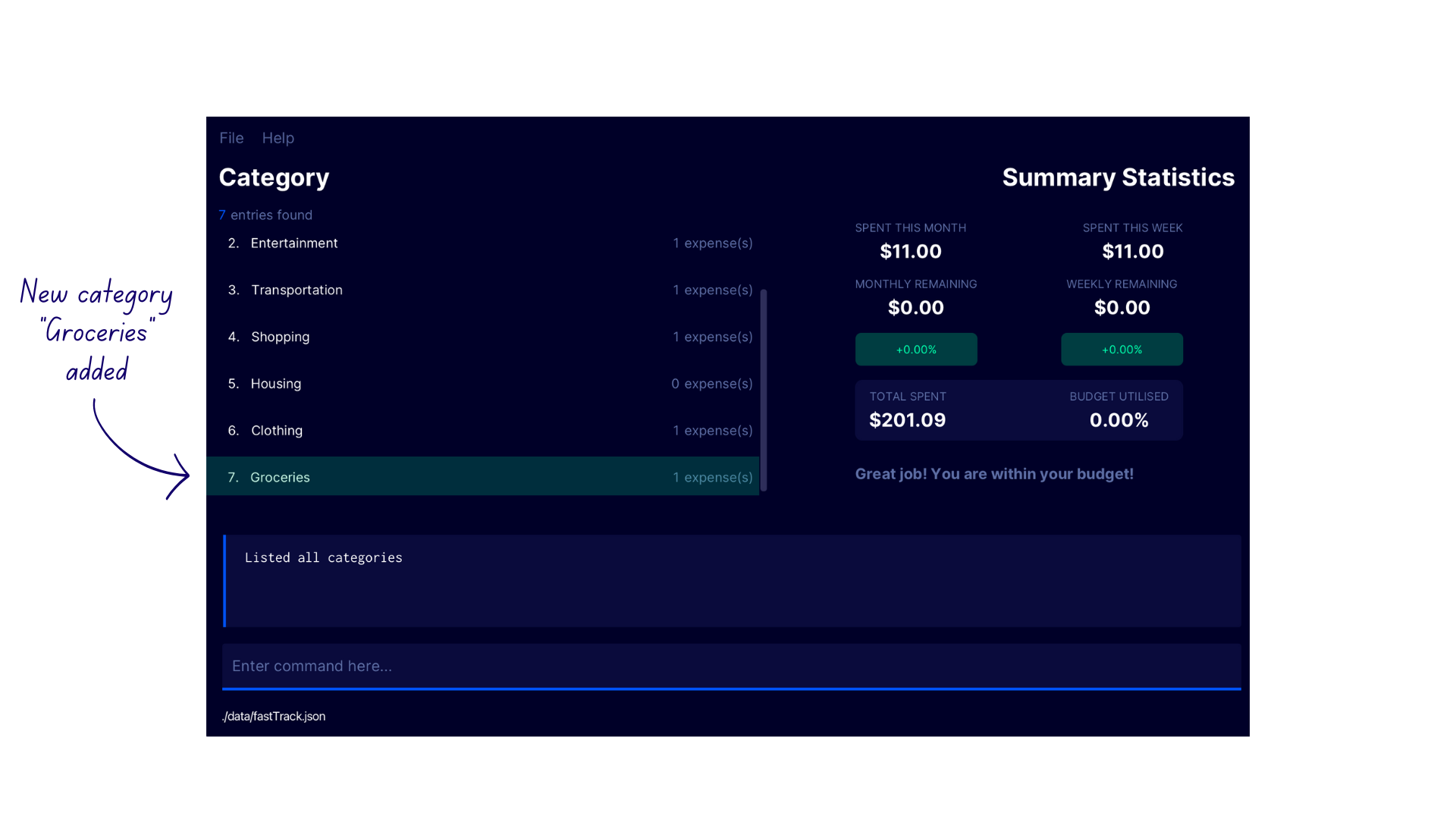
- Enter the command
lcatto switch to the Category Display. Notice how FastTrack has automatically created a new categoryGroceriesin the category list!
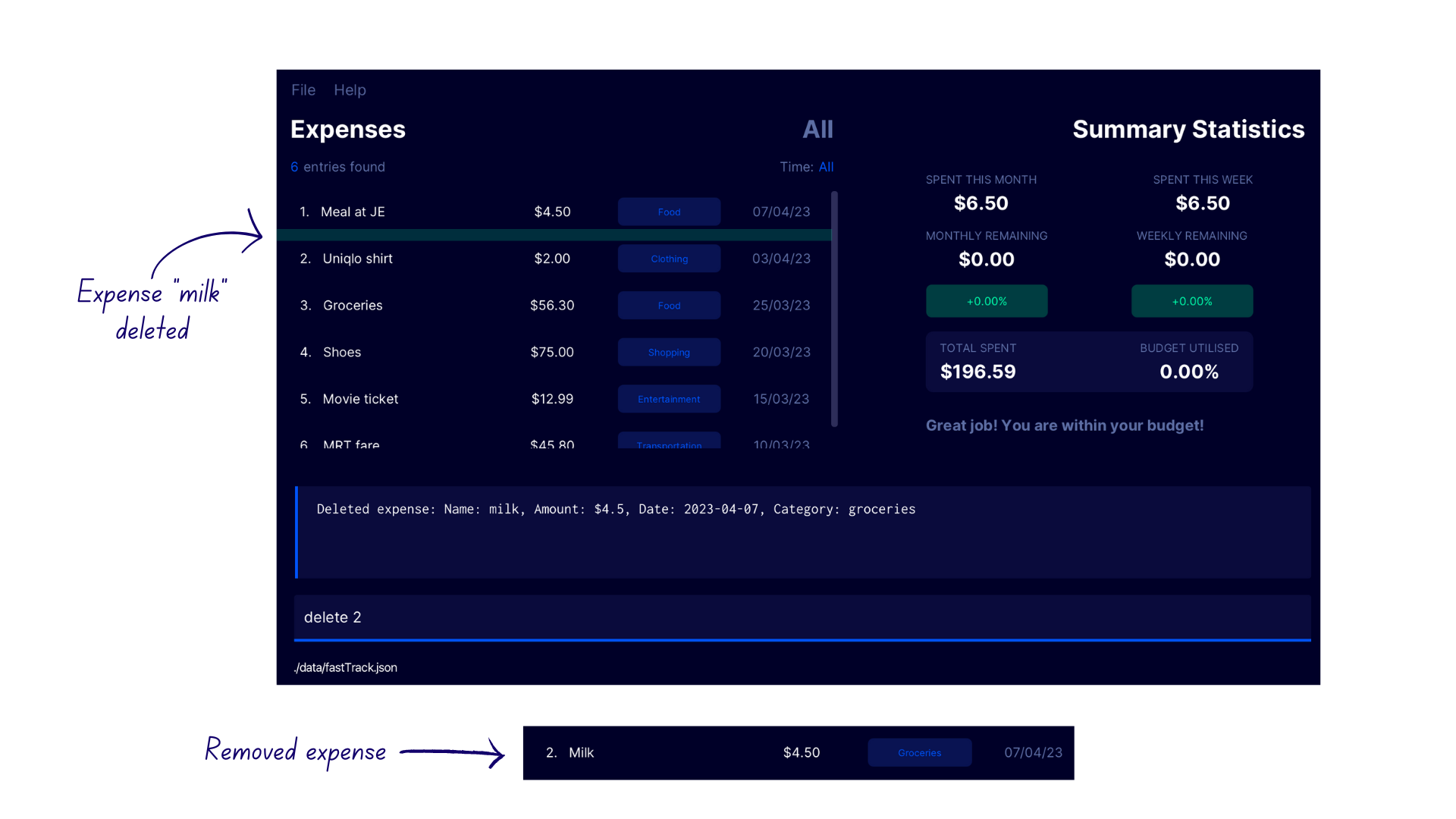
Deleting an expense delete
Deletes an expense at the specified INDEX in the expense list.
Format: delete INDEX
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
INDEX |
The index number shown in the displayed categories list. It must be a positive integer i.e. 1, 2, 3, … |
Examples
-
listfollowed bydelete 2deletes the second expense in the expense list -
find moviefollowed bydelete 1deletes the first expense in the results of thefindcommand
Demonstration
- Type the command
listto switch to the Expense Display - Enter the command
delete 2into the command box - FastTrack deletes the second expense in the expense list with the confirmation message
Deleted expense: Name: milk, Amount: $4.5, Date: 2023-04-07, Category: groceries.
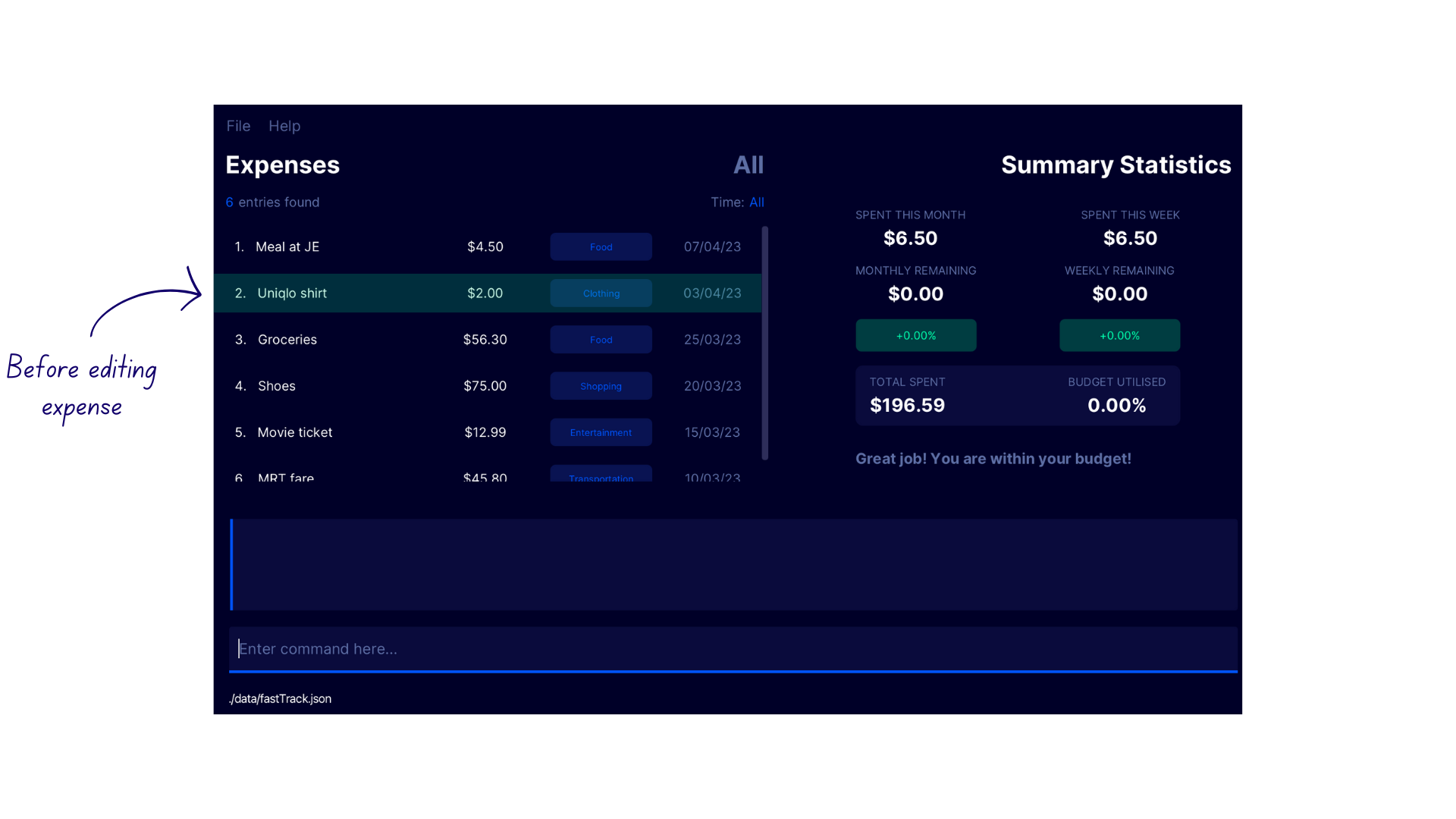
Editing an expense edexp
Edits the expense at the specified INDEX in the expense list.
Format: edexp INDEX [c/CATEGORY_NAME] [n/EXPENSE_NAME] [d/DATE] [p/PRICE] [r/RECUR_PERIOD]
Every parameter except for INDEX is optional by themselves, but at least one of them must be specified in addition
to INDEX, otherwise the command will not be executed.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
INDEX |
The index of the expense to be edited. It must be a positive integer i.e. 1, 2, 3, … |
CATEGORY_NAME |
The new category name of the expense to be changed to. This parameter is optional. |
EXPENSE_NAME |
The new expense name of the expense to be changed to. This parameter is optional. |
DATE |
The new date of the expense to be changed to. The date format should be d/m/yyyy. This parameter is optional. |
PRICE |
The new price of the expense to be changed to. The specified price should be a number, e.g. 4, 4.50. This parameter is optional. |
Examples
-
edexp 1 c/grocerieschanges the category of the first expense in the expense tracker -
edexp 2 p/20 n/movie nightchanges the price and name of the second expense in the expense tracker
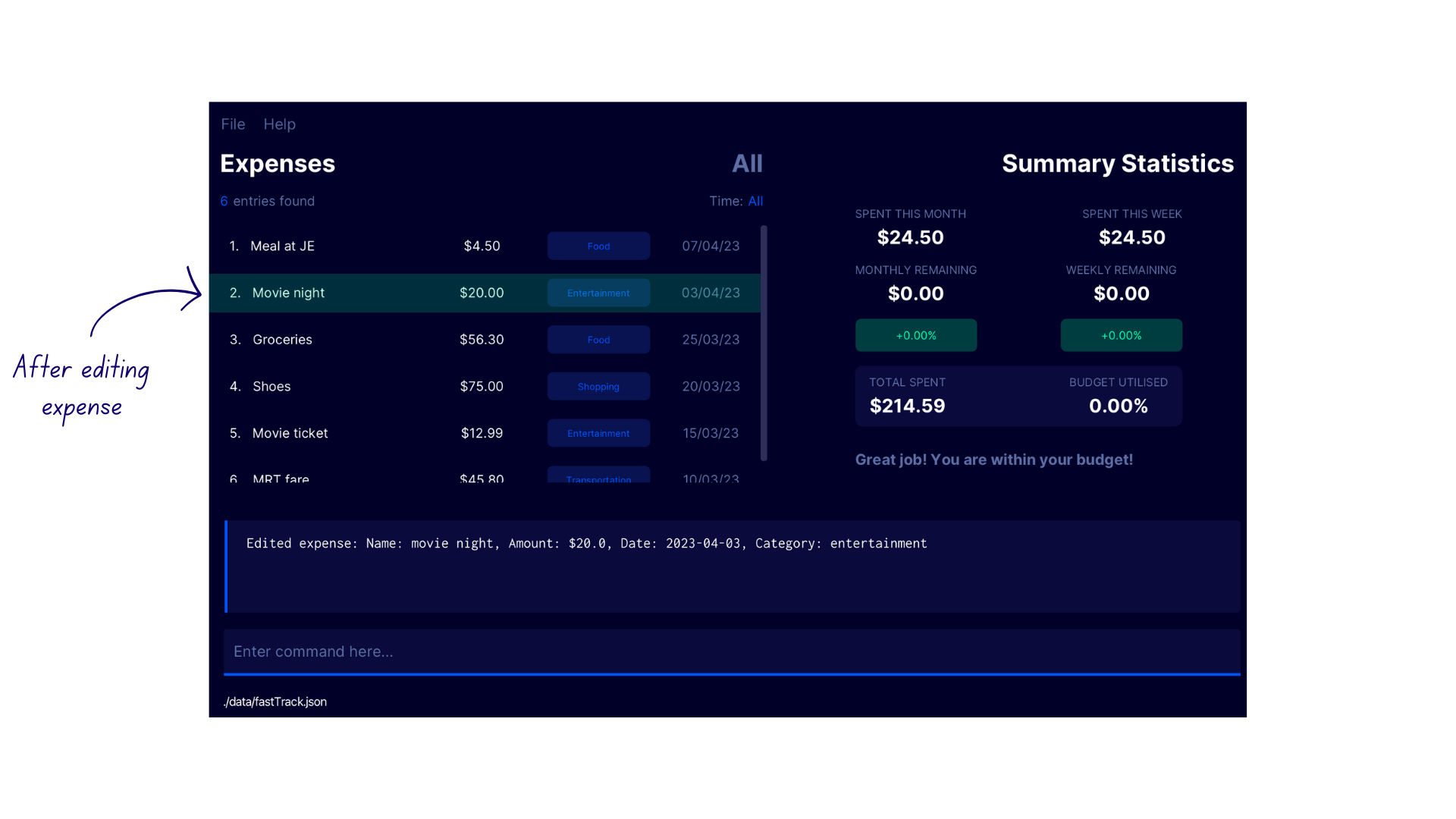
Demonstration
- Type the command
listto switch to the Expense Display - Enter the command
edexp 2 p/20 n/movie night c/entertainment - FastTrack edits the second expense in the expense list with the confirmation message
Edited expense: Name: movie night, Amount: $20.0, Date: 2023-04-03, Category: entertaiment.
Search for an expense by keyword find
Find expenses whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
dinnerwill matchDinner - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
ramen Dinnerwill matchDinner ramen - Only the name of the expense is searched
- Only full words will be matched e.g.
dinnwill not matchdinner - Expenses matching at least one keyword will be returned
e.g.
movie dinnerwill returndinner with Alex,movie with friends
Examples
Suppose you have 3 expenses logged:
Date: 2023-03-02, Category: Food, Name: McDonald's, Price: $7.50
Date: 2023-03-02, Category: Food, Name: KFC, Price: $6.00
Date: 2023-03-03, Category: Groceries, Name: Milk, Price: $4.00
-
find kfc milkreturnsMilkandKFC -
find mcdonald'sreturnsMcDonald's
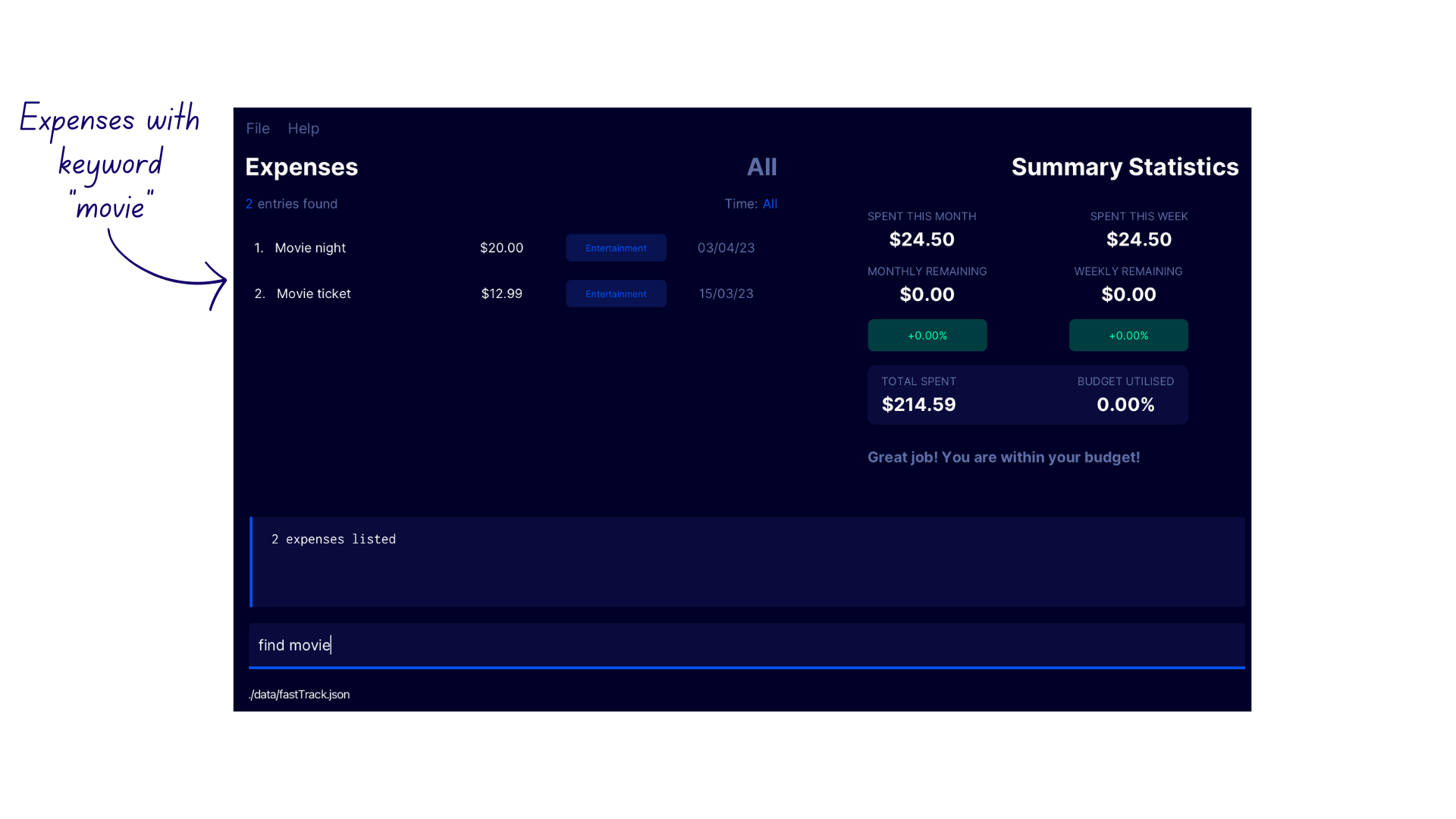
Demonstration
- Enter the command
find movieinto the command box to find expenses with the keywordmovie - FastTrack filters the expense list to show only the expenses matching the given keyword, with the confirmation message
Edited expense: Name: movie night, Amount: $20.0, Date: 2023-04-03, Category: entertaiment.
Recurring Expenses
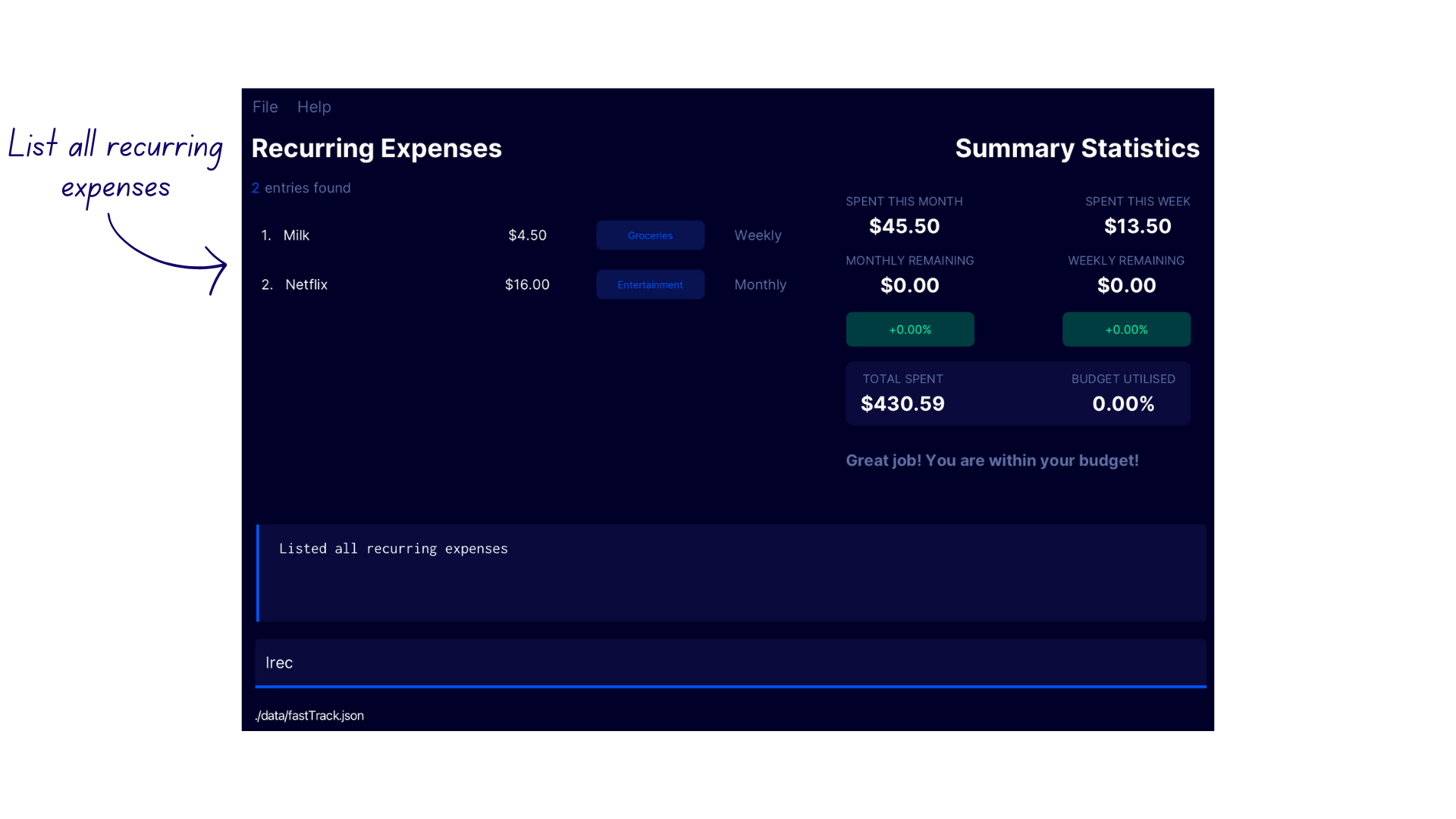
Listing Recurring Expenses lrec
Displays the list of recurring expenses in FastTrack.
Format: lrec
Demonstration
- Type
lrecinto the command box - FastTrack displays the list of recurring expenses with the confirmation message
Listed all recurring expenses
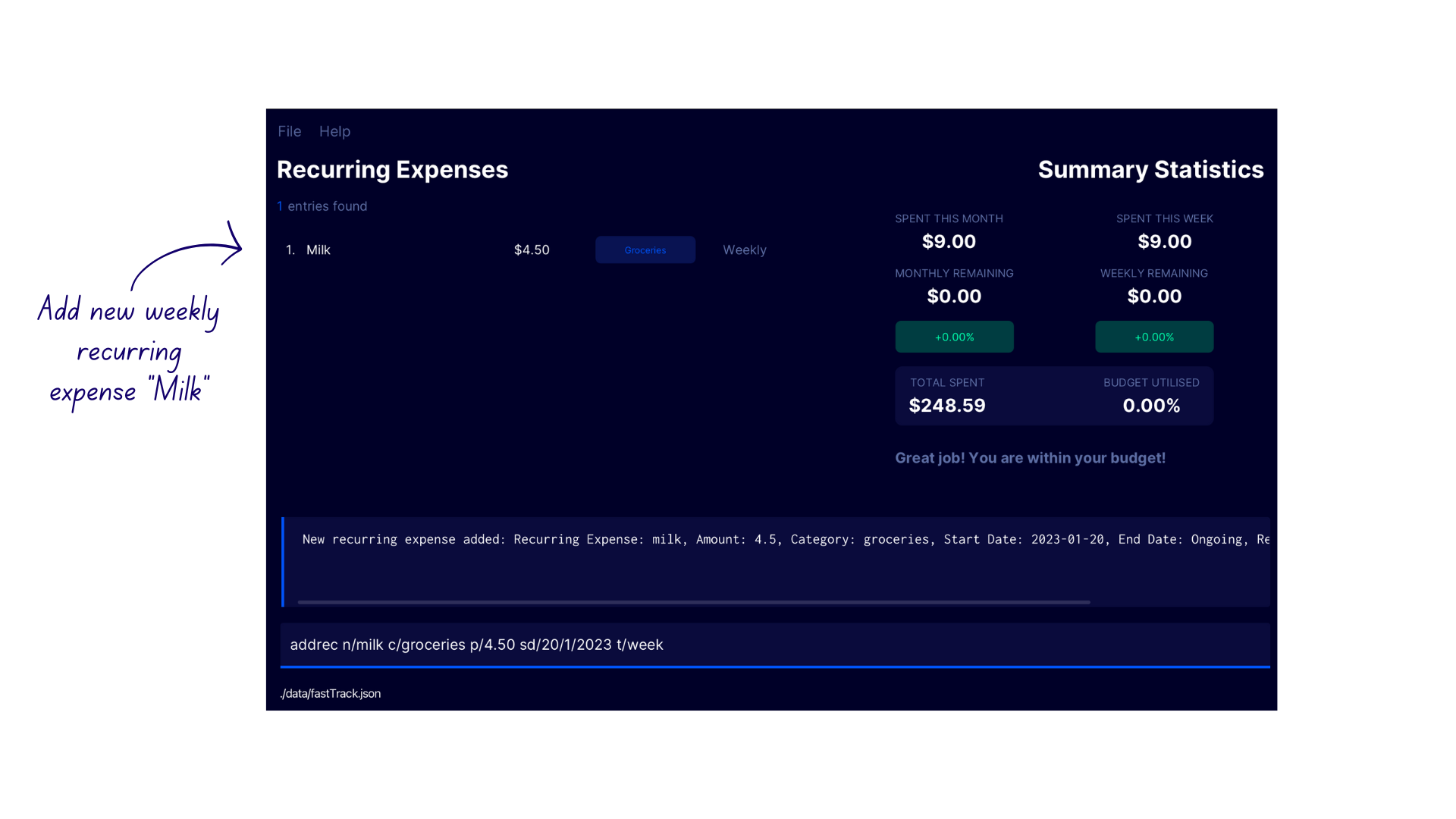
Adding a Recurring Expense addrec
Adds a recurring expense to FastTrack.
Format: addrec c/CATEGORY_NAME n/ITEM_NAME p/PRICE t/INTERVAL sd/START_DATE [ed/END_DATE]
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
CATEGORY_NAME |
The category which the recurring expense should be classified under. If there is no such category, a new category will be created with the specified category name. |
ITEM_NAME |
Name of the recurring expense being added. |
PRICE |
The price of the recurring expense being added. The specified price should be a number, e.g. 4, 4.50. |
INTERVAL |
The period with which the expense is recurring. The timeframes available are: 1. day 2. week 3. month 4. year
|
START_DATE |
The starting date of the recurring expense. The date format should be d/m/yyyy. |
END_DATE |
The ending date of the recurring expense. The date format should be d/m/yyyy. This parameter is optional. |
![]() Info
Info
Note that once a recurring expense is added, it automatically adds a series of expenses to the expense list at the specified interval until the END_DATE. If an END_DATE is not yet specified, the expenses will be added up to the current date.
![]() Tip:
Tip:
FastTrack’s recurring expense feature is designed to help you keep track of regular expenses that occur at a fixed interval, such as monthly subscription fees or cloud storage bills. By setting up a recurring expense, you save precious time and effort by automating the process of adding these expenses to FastTrack.
![]() Caution
Caution
Avoid setting an END_DATE that is too far in the future or a START_DATE that is too far in the past. Setting a date range that spans a large number of years or generates a large number of expenses may cause FastTrack to become temporarily unresponsive.
For example, if the current date is 3/2/2023 and the START_DATE is set to 3/2/2000 with an INTERVAL of day, this will generate over 8,000 expenses and may cause performance issues.
Examples
addrec n/milk c/groceries p/4.50 sd/20/3/2023 t/monthaddrec n/milk c/groceries p/4.50 sd/20/3/2023 ed/15/5/2023 t/w
Demonstration
- Enter the command
addrec n/milk c/groceries p/4.50 sd/20/1/2023 t/weekto create a weekly recurring expense starting on 20/1/2023. - FastTrack creates the new recurring expense with the confirmation message
New recurring expense added: Recurring Expense: milk, Amount: 4.5, Category: groceries, Start Date: 2023-01-20, End Date: Ongoing, Recurring Expense Type: WEEKLY
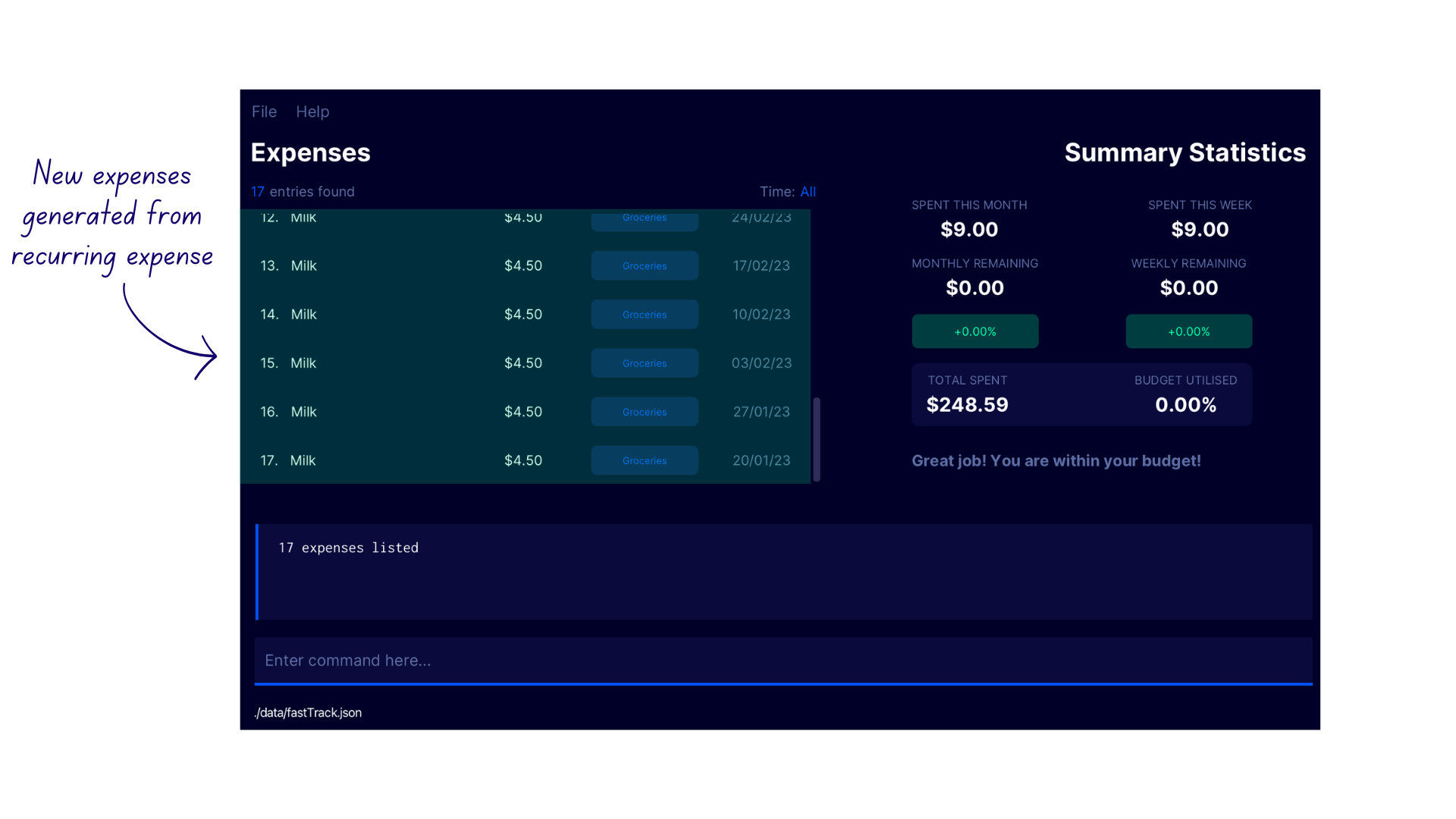
- Enter the command
listto switch to the Expense Display. Notice that FastTrack has automatically added the weekly expenses in the expense list!
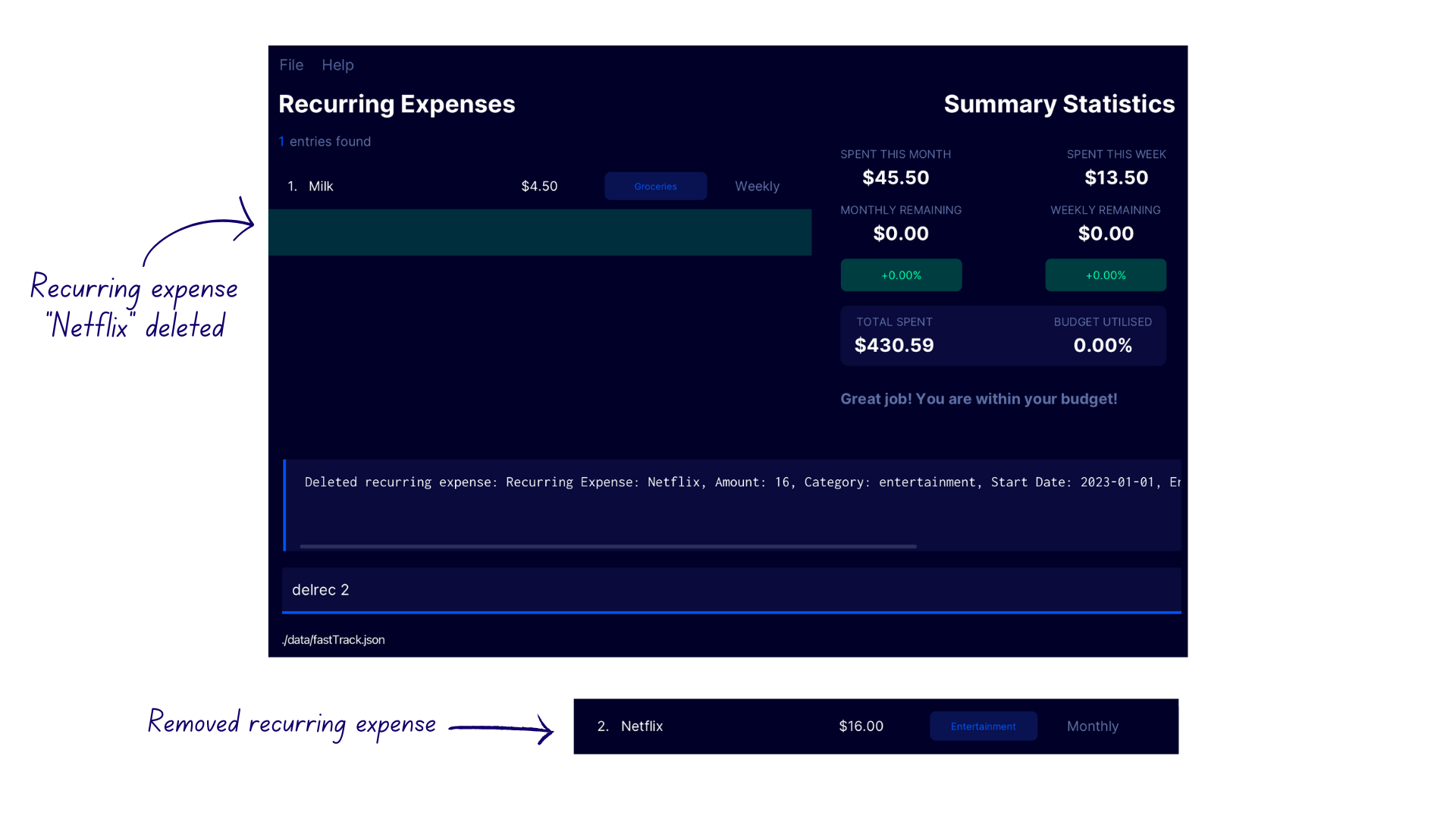
Deleting a recurring expense delrec
Deletes an expense category at the specified INDEX in the recurring expense list.
Format: delrec INDEX
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
INDEX |
The index number shown in the displayed recurring expense list. It must be a positive integer i.e. 1, 2, 3, … |
Examples
-
lrecfollowed bydelrec 2deletes the second recurring expense in the recurring expense list -
lrecfollowed bydelrec 1deletes the first recurring expense in the recurring expense list
Demonstration
- Enter the command
lrecto switch to the Recurring Expense Display - Enter the command
delrec 2 - FastTrack deletes the second recurring expense in the recurring expense list with the confirmation message
Deleted recurring expense: Recurring Expense: Netflix, Amount: 16, Category: entertainment, Start Date: 2023-01-01, End Date: Ongoing, Recurring Expense Type: MONTHLY.
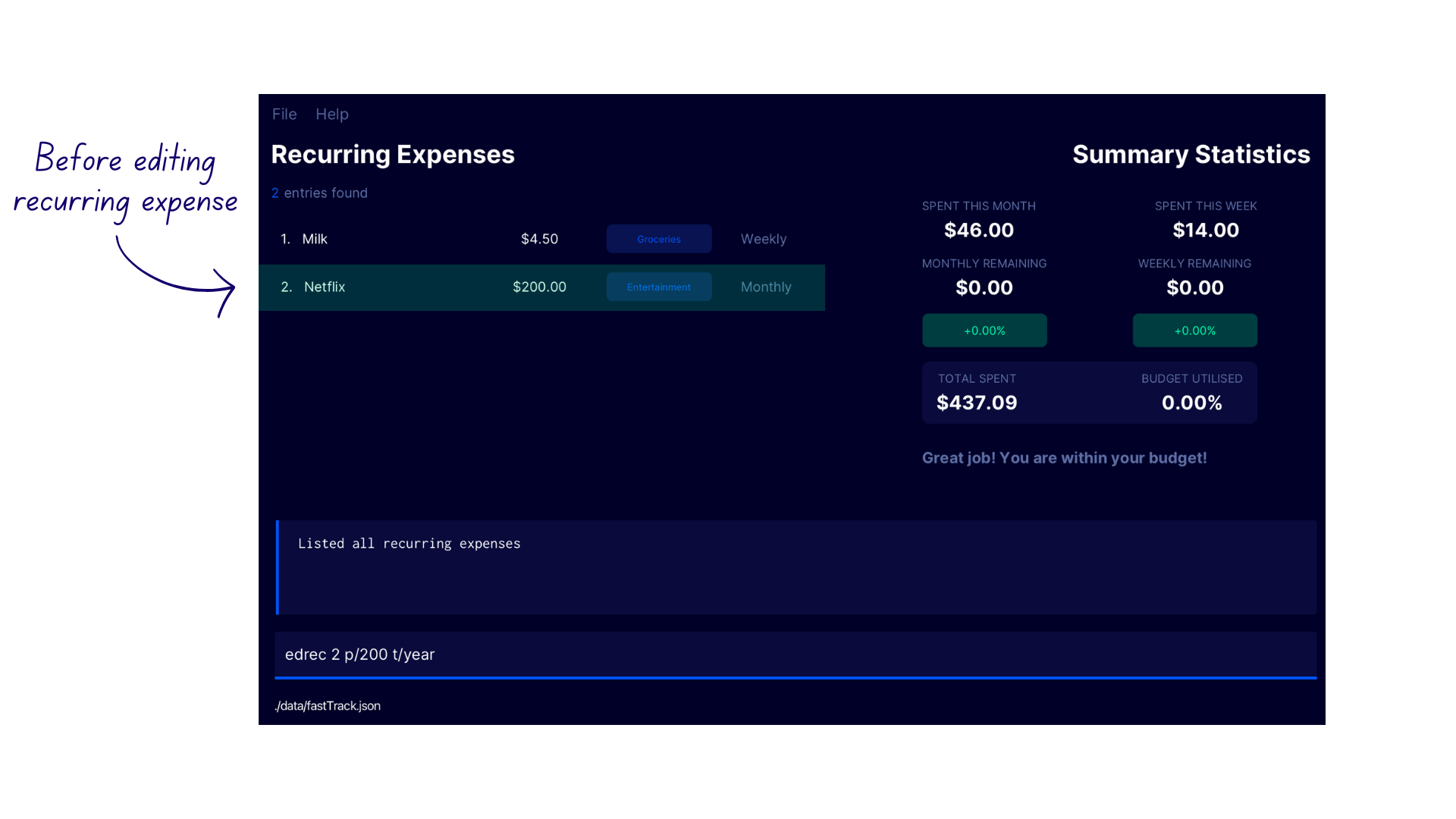
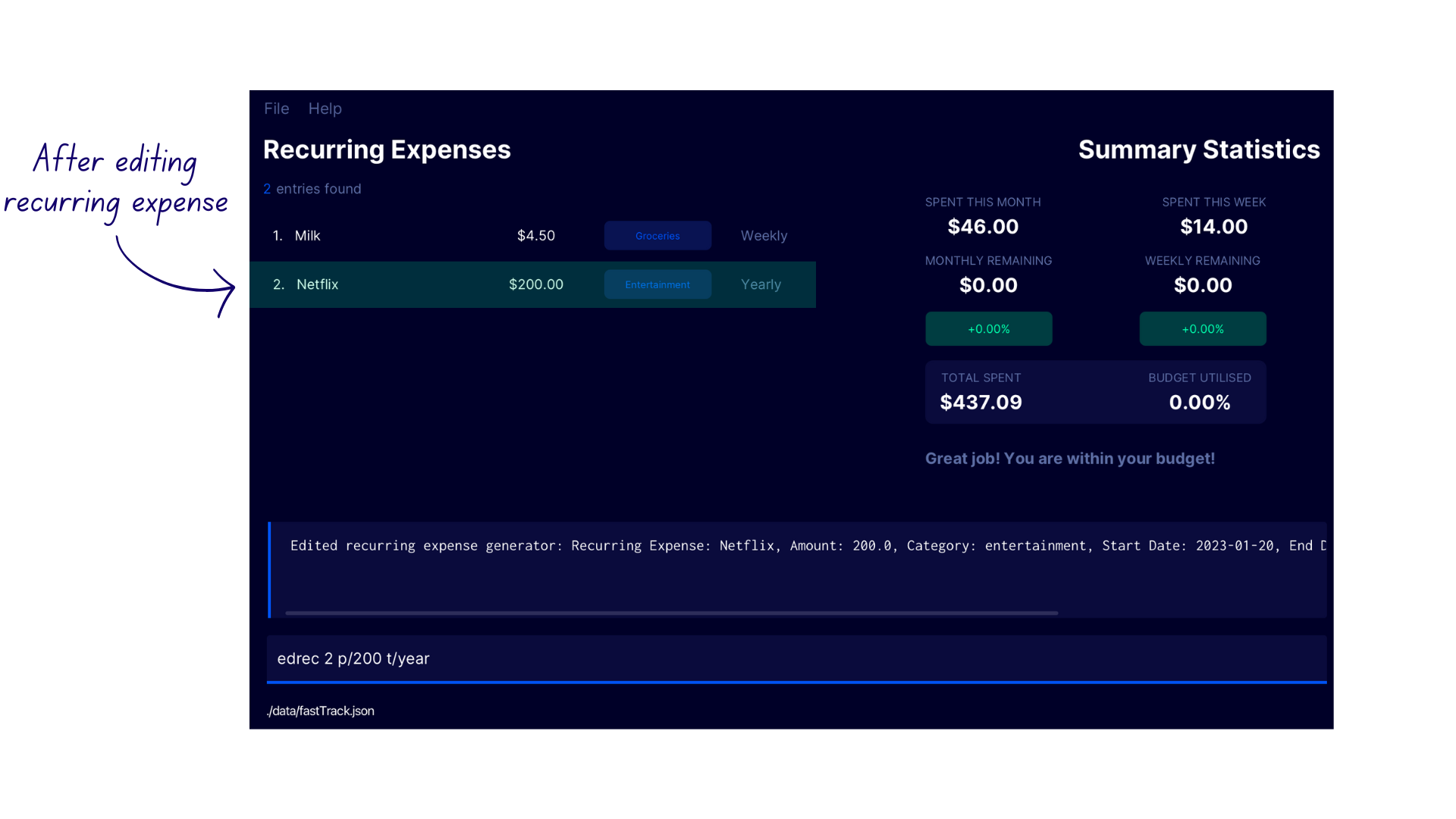
Editing a recurring expense edrec
Edits the expense at the specified INDEX
Format: edrec INDEX [c/CATEGORY_NAME] [n/EXPENSE_NAME] [p/PRICE] [t/INTERVAL] [ed/END_DATE]
Every parameter except for INDEX is optional by themselves, but at least one of them must be specified in addition
to INDEX, otherwise the command will not go through.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
INDEX |
The index of the recurring expense to be edited. It must be a positive integer i.e. 1, 2, 3, … |
CATEGORY_NAME |
The new category name of the recurring expense to be changed to. This parameter is optional. |
EXPENSE_NAME |
The new expense name of the recurring expense to be changed to. This parameter is optional. |
PRICE |
The new price of the recurring expense to be changed to. The specified price should be a number, e.g. 4, 4.50. This parameter is optional. |
INTERVAL |
The new recurrence period of the expense to be changed. The timeframes available are: 1. day 2. week 3. month 4. yearThis parameter is optional. |
END_DATE |
The new ending date of recurring expense. The date format should be d/m/yyyy. This parameter is optional. |
![]() Caution
Caution
If you want to stop a recurring expense before its intended END_DATE, make sure to delete it before the current date.
If you edit the recurring expense to end before the current date, this only prevents new expenses from being added, but expenses that were previously generated will still exist in FastTrack.
Examples
-
edrec 1 c/groceries t/weekupdates the category and recurrence period first recurring expense in the expense tracker. -
edrec 2 p/4.50 ed/15/5/2023updates the price and ending date of the second recurring expense in the expense tracker.
Demonstration
- Enter the command
lrecto switch to the Recurring Expense Display. - Say you have upgraded to a Netflix yearly subscription plan - enter the command
edrec 2 p/200 t/year. - FastTrack edits the second recurring expense in the recurring expense list with the confirmation message
Edited recurring expense generator: Recurring Expense: Netflix, Amount: 200.0, Category: entertainment, Start Date: 2023-01-20, End Date: Ongoing, Recurring Expense Type: YEARLY.
General Features
Command Summary
| Feature | Command Format | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Set Budget | set p/AMOUNT |
set p/1000 |
| Help | help |
help |
| Exit program | exit |
exit |
| Clear data | CLEAR |
CLEAR |
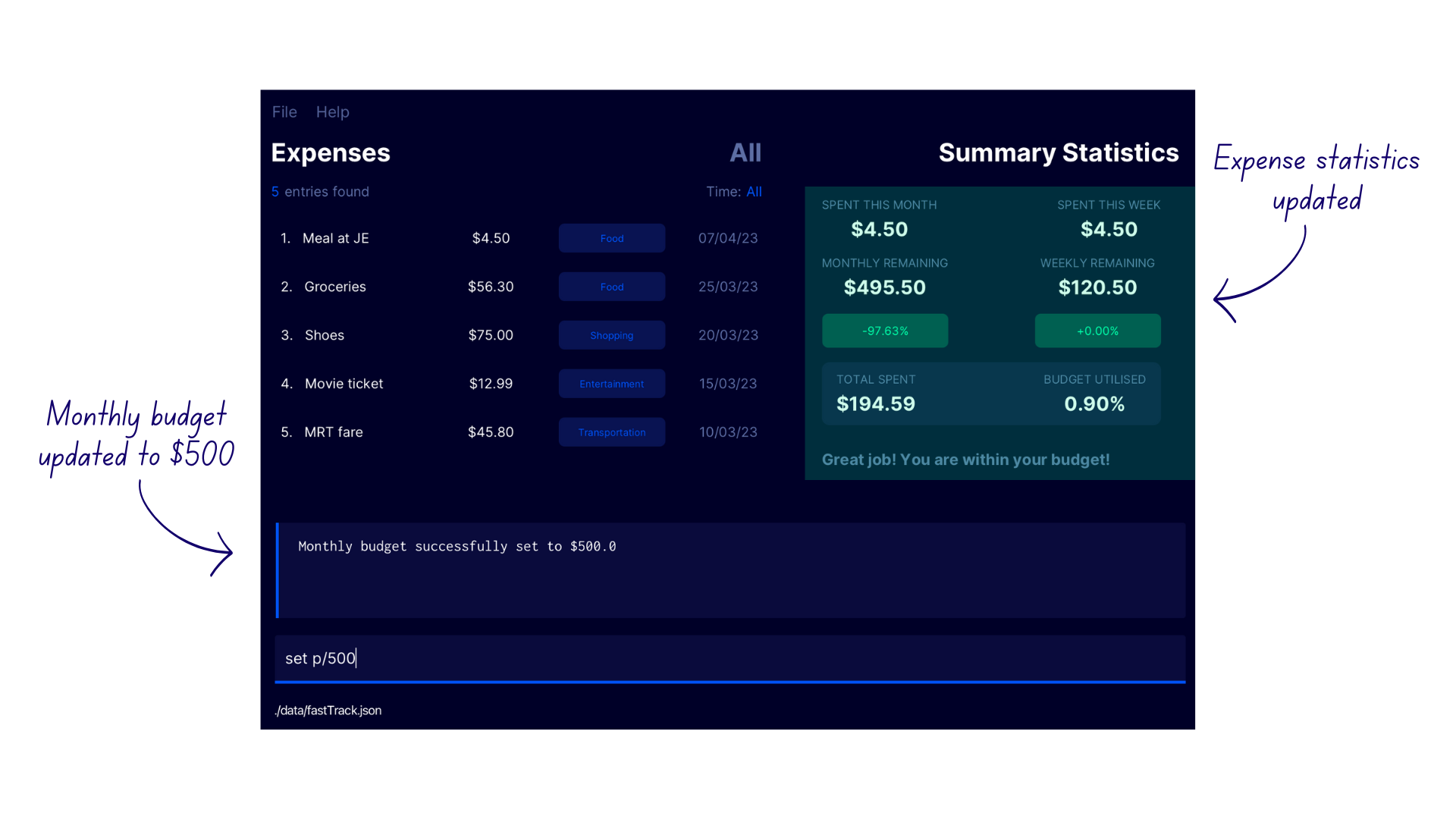
Setting A Budget set
Sets a monthly budget for FastTrack. For first-time users of FastTrack, no budget is set and expense statistics are not updated.
In order to view all the expense statistics, you must first set a budget using this command.
FastTrack derives the weekly budget from this monthly budget by dividing the monthly budget by 4.
Format set p/AMOUNT
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
AMOUNT |
The monthly budget amount to set. The specified budget should be a number, e.g. 4, 4.50. |
![]() Caution
Caution
FastTrack does not allow setting a budget of $0.
Examples
-
set p/500sets the monthly budget of FastTrack to $500.
Demonstration
- Enter the command
set p/500to set the monthly budget of FastTrack to $500. - FastTrack updates the monthly budget to $500 with the confirmation message
Monthly budget successfully set to $500.0
Category Autocompletion
FastTrack offers a powerful and time-saving feature that autocompletes your category names for you! When you start typing c/, FastTrack provides a list of suggested category names as a popup above the command box.
Give it a try and see how much time you can save with this feature!
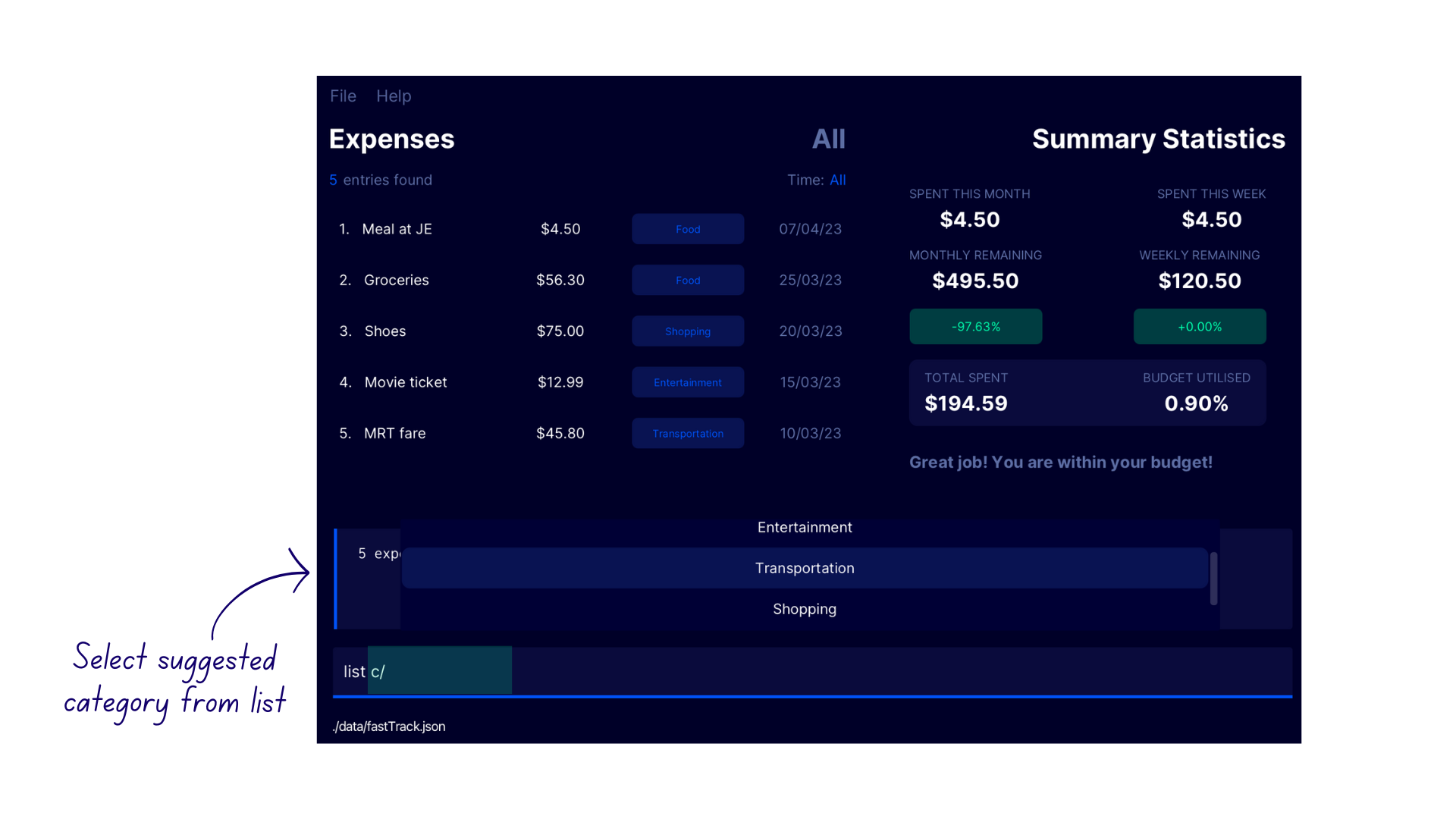
How to Use Category Autocompletion?
- Type
c/in the command box to trigger the autocompletion feature. - FastTrack will display a list of suggested category names above the command box.
- To select a category name from the list, use the
UPandDOWNarrow keys to navigate through the suggestions list. - Press
ENTERto autocomplete the selected category name. - If the category you’re looking for is conveniently at the bottom of the list, simply press
TABto autocomplete the first suggested category without having to navigate through the list manually! - If you decide not to use any of the suggested categories, just continue typing your own category name as per normal.
![]() Tip:
Tip:
Want to use TAB directly without navigating inside the suggestion list?
Narrow down the list of suggested categories by typing the first few words of your desired category name. Once the option appears at the bottom of the list, simply press TAB for autocompletion.
![]() Caution
Caution
To use category autocompletion, make sure that c/ is the last text you’ve entered into the command box.
If there is any other text in front of c/, the autocompletion feature will be disabled.
Demonstration
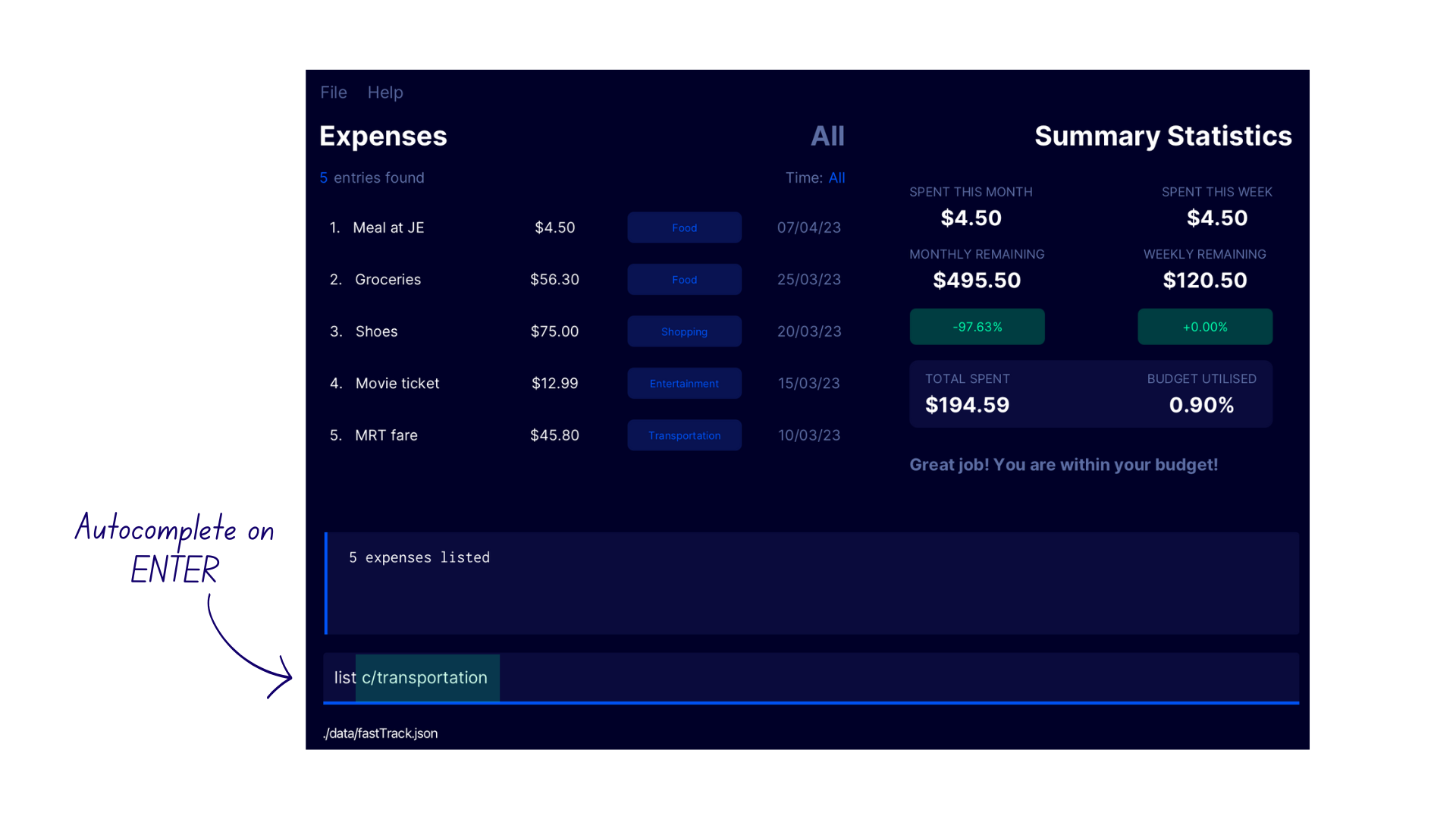
- Enter
list c/into the command box. - A list of suggested categories appear in a popup above the command box.
- Navigate into the suggestion list using the
UParrow key and pressENTERon the desired categoryTransportation. - This autocompletes the category name.
- If you need to navigate out of the suggestion list, press the
DOWNarrow key until the cursor returns to the command box.
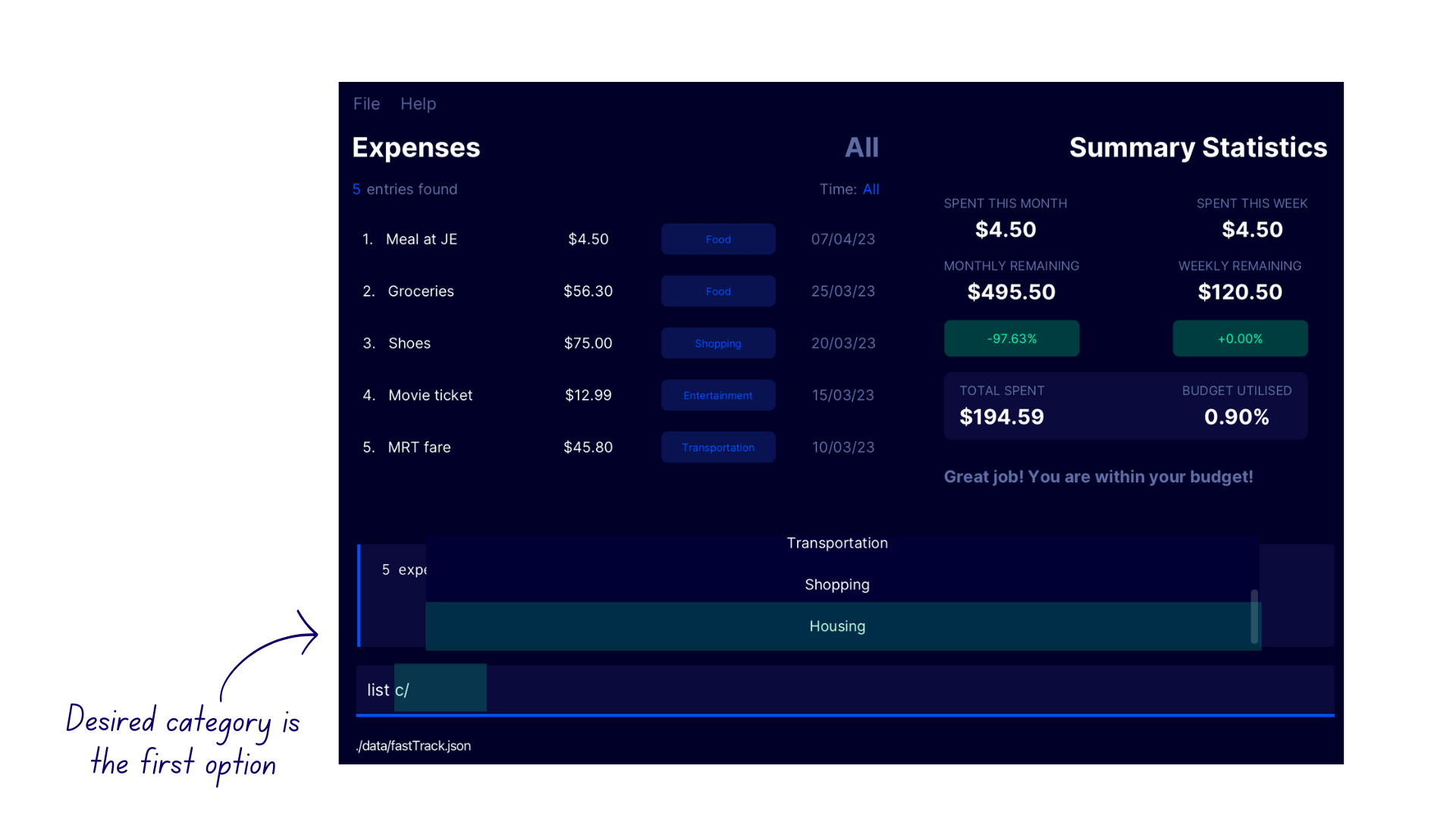
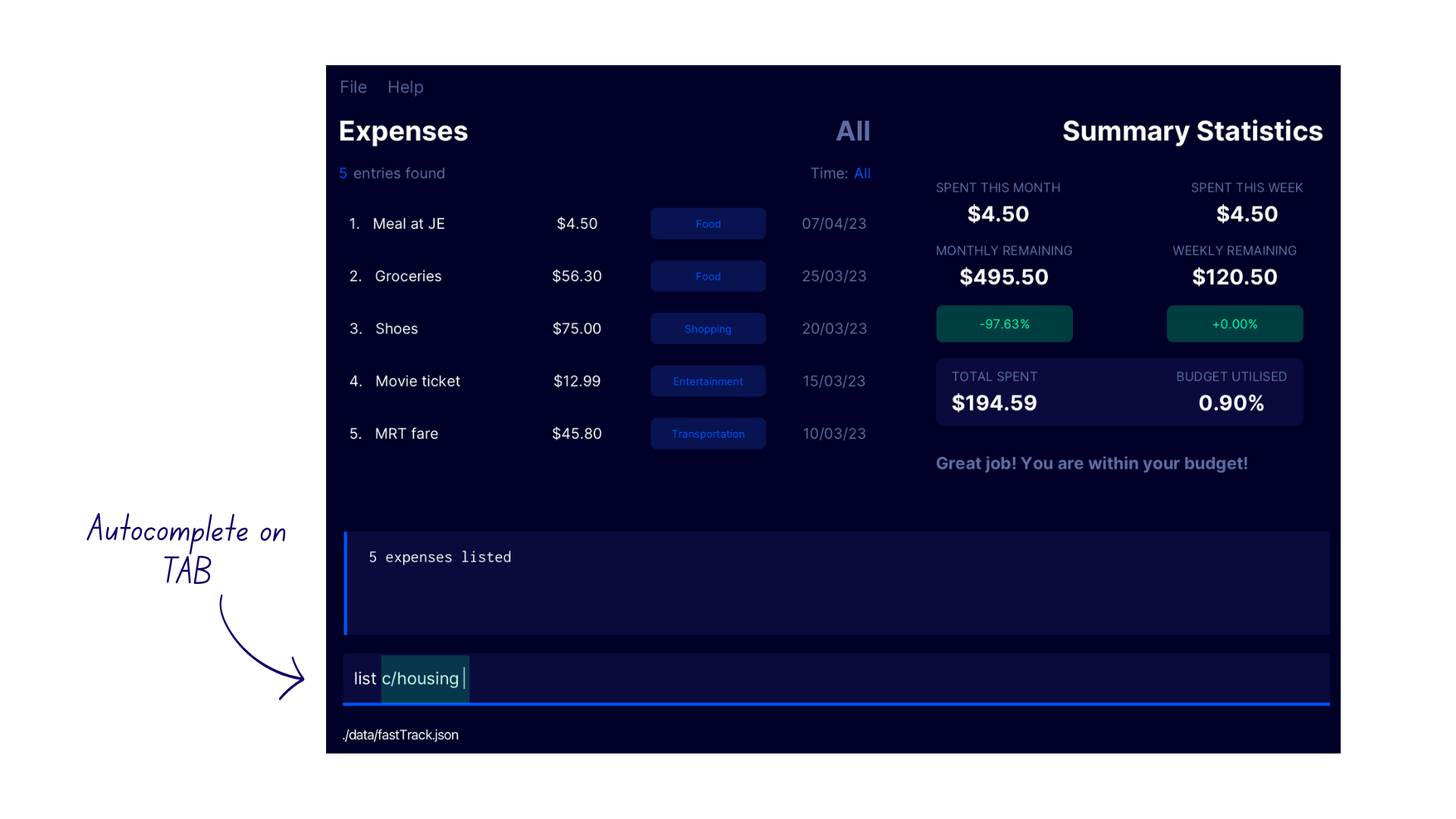
- Enter
list c/into the command box. - A list of suggested categories appear in a popup above the command box.
- If the desired category
Shoppingis the first suggestion in the list (the bottom-most suggestion), pressTABwithin the command box. - This autocompletes the category name.
Clearing all entries CLEAR
Clears all entries from FastTrack. This command removes all stored expenses, recurring expenses and categories.
Format: CLEAR
![]() Caution
Caution
This command will delete all the data stored in FastTrack apart from the stored monthly budget. To minimise the risk of accidentally using this command, we have made it such that the command only works when the word CLEAR is fully uppercase.
Exercise caution before using this command.
Demonstration
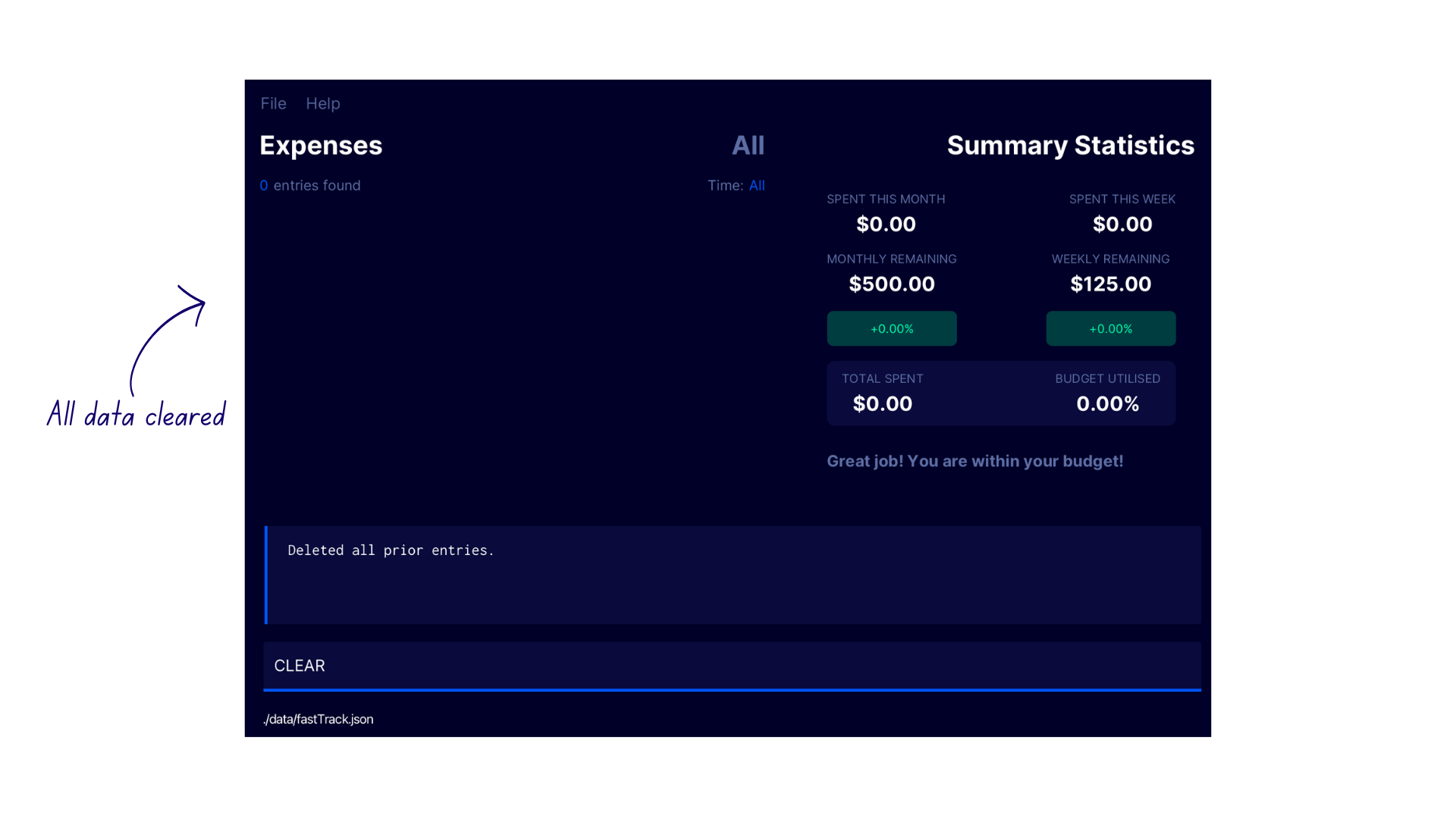
- Enter
CLEARin the command box. - FastTrack clears all previously logged expenses, recurring expenses and categories, with the confirmation message
Deleted all prior entries.
Exiting FastTrack exit
After logging your expenses, you might want to close the application and ensure your data is saved.
This command closes FastTrack and saves the data to the fastTrack.json file located on computer’s hard disk.
Format: exit
Viewing help help
Shows a message explaining how to access the help page, as well as a quick rundown of what commands can be used.
Format: help

Expense Statistics Feature
FastTrack provides you with real-time statistics on your spending to help you keep track of your monthly budget. Here are the types of statistics displayed and what they mean.
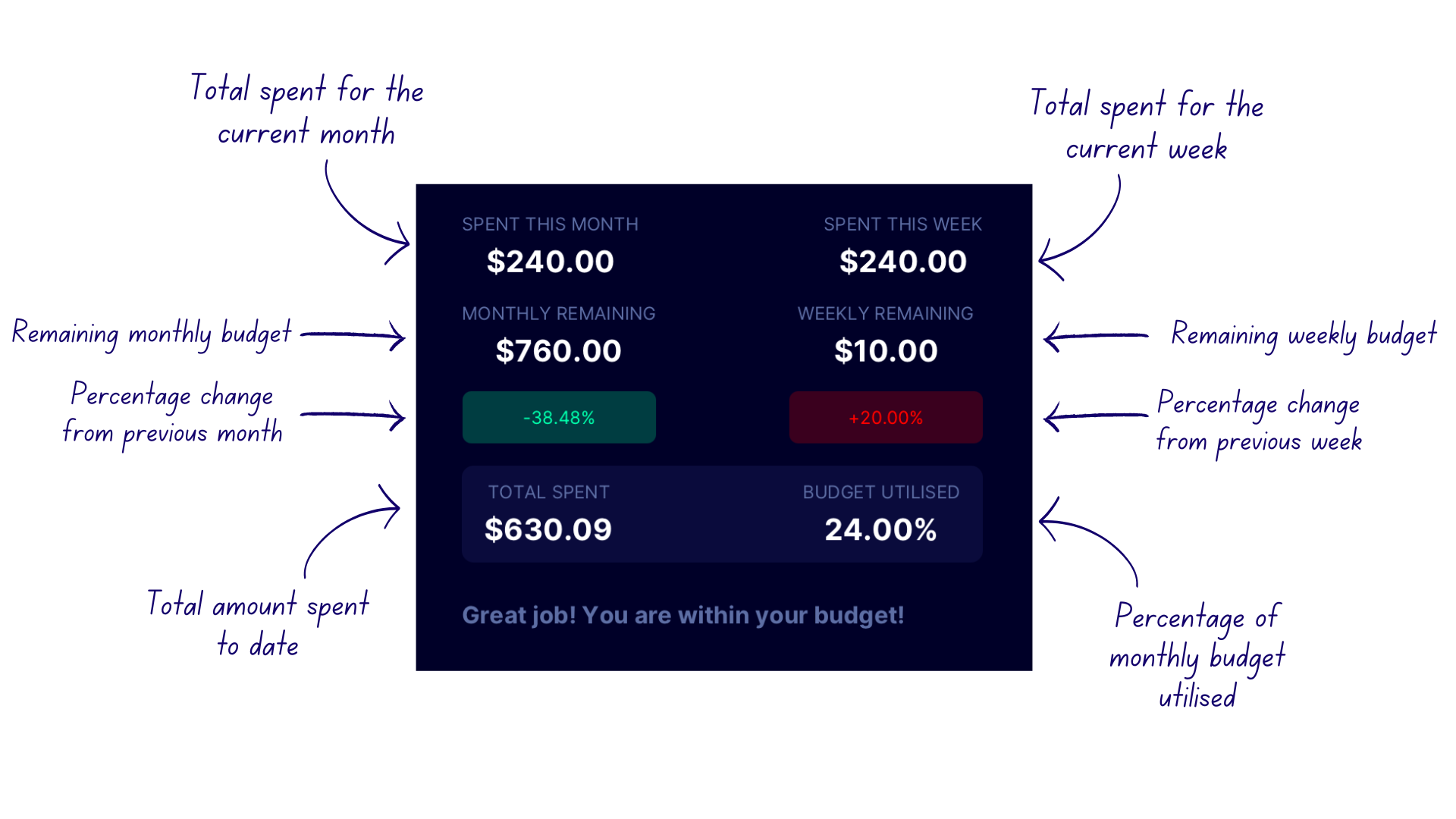
Monthly spending statistic
This statistic represents the total amount of money you have spent in the current month. It includes all expenses recorded in the current month.
For example, if the current month is March, this statistic shows the total amount of money spent in March.
Monthly remaining statistic
This statistic represents the amount of money you have left from your monthly budget. It gives you an idea of how much money you have left to spend for the rest of the month.
Monthly percentage change statistic
This statistic represents the percentage increase or decrease in your monthly spending relative to the previous month. The indicator colour is red if it is a percentage increase and green if it is a percentage decrease.
For example, if you spent $500 last month and $750 this month, the monthly percentage change indicator would be +50.00% and be displayed in a red colour.
If you spent $750 last month and $500 this month, the monthly percentage change would be -33.30% and be displayed in a green color.
Weekly spending statistic
This statistic represents the total amount of money you have spent in the current week, starting from Monday to Sunday. This gives you an idea of how much money you are spending on a weekly basis.
Weekly remaining statistic
This statistic represents the amount of money you have left from your weekly budget. Your weekly budget is the value of your monthly budget divided by four. This gives you an idea of how much money you have left to spend for the rest of the week.
Even if you have exceeded your previous week’s budget, this statistic will show that you have more remaining, as the weekly budget is fixed based on the monthly budget. Therefore, it is important to use this value as an estimate and not solely rely on it for your spending decisions!
Weekly percentage change statistic
This statistic represents the percentage increase or decrease in your weekly spending relative to the previous week. The indicator colour is red if it is a percentage increase and green if it is a percentage decrease.
For example, if you spent $500 last week and $750 this week, the weekly percentage change indicator would be +50.00% and be displayed in a red colour.
If you spent $750 last week and $500 this week, the weekly percentage change would be -33.30%.
Total spent statistic
This statistic represents the total amount of money you have spent to date, starting from the first expense you recorded in FastTrack.
This gives you an idea of how much money you have spent over the period of time from when you started tracking your expenses.
Budget utilisation percentage statistic
This statistic represents the percentage of your monthly budget that you have already utilised in the current month.
For example, if your monthly budget is $1000, and you have already spent $500, your budget utilised percentage would be 50%.
This gives you an idea of how much of your monthly budget you have used up.
![]() Caution
Caution
Even if you have exceeded your budget, this statistic will reflect that you have fully utilised your budget, and will remain at 100%.
Saving the data
All data in FastTrack are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
FastTrack’s data are saved as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/fastTrack.json. Advanced users who are familiar with JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous FastTrack home folder.
Q: Does FastTrack require a Wi-Fi network?
A: No, FastTrack does not need any sort of internet connection to run! You can be rest assured that your data is kept safe locally on your computer. However, accessing the user guide and developer guide which are hosted online will require an internet connection.
Q: Why are some of my expenses being categorised as Misc?
A: Misc is an internal default category in FastTrack that represents an unclassified expense. If you see an expense with the Misc category, chances are, the category it was previously associated with was deleted.
Q: My expense name gets cut off with trailing ellipses ..., how do I fix this?
A: Try resizing the FastTrack window size by increasing its width until the full expense names are within view.
Q: Can I set reminders for recurring expenses in FastTrack?
A: No, FastTrack does not currently have a built-in feature for setting reminders for recurring expenses.
However, you can use an external calendar or reminder app to keep track of recurring expenses.
Q: Does FastTrack integrate with payment systems like credit cards or PayPal?
A: Currently, FastTrack does not support integration with external payment systems. However, we are constantly improving and expanding our features, and we plan to explore integrating with popular payment systems in the future. Stay tuned for more updates!